平台总线---深入分析
阅读引言:本文会从平台总线的介绍,注册平台设备和驱动, 源码分析, 总结五个部分展开, 源码分析platform放在了最后面。
目录
一、平台总线介绍
二、平台总线如何使用
三、平台总线是如何工作的
四、注册platform设备
五、注册platform驱动
六、编写probe函数
七、平台总线源码分析
一、平台总线介绍
平台总线模型也叫platform总线模型。平台总线是Linux系统虚拟出来的总线。所谓虚拟出来的总线其实就是使用软件来模拟物理总线的一些性质, linux各种子系统还是别的, 都特别爱玩匹配这套东西, 挺好。
二、平台总线如何使用
平台总线模型将一个驱动分成了俩个部分,分别是device.c和driver.c,用来描述device.c硬件,driver. c 用来控制硬件。这样做的目的主要是为了提高代码的重复利用性, 降低耦合度。
三、平台总线是如何工作的
平台总线通过字符串比较,将name相同的device.c和driver.c匹配到一起来控制硬件。平台总线原则:先分离,后搭档。
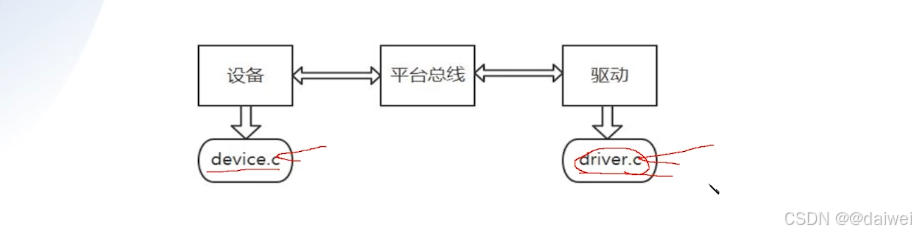
note:源码分析这个位置放在后面些
四、注册platform设备
platform设备驱动(device.c)里面写的是硬件资源。这里的硬件资源指的是寄存器地址,中断号以及其他硬件资源等。在linux内核里面用struct platform_device结构体来描述硬件资源。这个结构体定义在include/linux/platform_device.h文件当中,结构体原型如下:
struct platform_device {const char *name;int id;bool id_auto;struct device dev;u64 platform_dma_mask;struct device_dma_parameters dma_parms;u32 num_resources;struct resource *resource;const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;/** Driver name to force a match. Do not set directly, because core* frees it. Use driver_set_override() to set or clear it.*/const char *driver_override;/* MFD cell pointer */struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;/* arch specific additions */struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};name可以匹配, 也可以在sys/bus/devices下展示。
/** Resources are tree-like, allowing* nesting etc..*/
struct resource {resource_size_t start;resource_size_t end;const char *name;unsigned long flags;unsigned long desc;struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child;
};资源的种类:ioport.h文件中

使用struct resource描述硬件资源信息示例:
struct resource my_dev_resource[] = {[0] = {.start = 0x1000, .end = 0x1000, .flags = IORESOURCE_MEM},[1] = {.start = 13, .end = 13, .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ}
};在my_dev_resource这个结构体数字中包含了俩组资源,第一组资源的类型是IORESOURCE_MEM,表示这组资源是一组内存类型的资源。起始地址是0xFDD60000,终止地址是0xFDD60004。第二组资源的类型是IORESOURCE_IRQ,表示这是一组中断资源, 中断很号是13。
platform设备加载和卸载函数
platform设备加载函数: 函数原型:int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *device) 函数作用:加载platform设备。
platform设备卸载函数: 函数原型:void platform_device_unregister(struct platform_device *device) 函数作用:卸载platform设备。
代码结构:
void my_dev_release(struct device *dev)
{printk("%s is called",__func__);
}struct resource my_dev_resource[] = {[0] = {.start = 0xFDD60000, .end = 0xFDD60004, .flags = IORESOURCE_MEM},[1] = {.start = 13, .end = 13, .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ}
};struct platform_device my_dev = {.name = "mydev",.id = -1,.resource = my_dev_resource,.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(my_dev_resource),.dev = {.release = my_dev_release},
};int __init my_dev_init(void)
{platform_device_register(&my_dev);
}void __exit my_dev_exit(void)
{platform_device_unregister(&my_dev);
}五、注册platform驱动
关键数据结构, platform设备驱动(driver.c)里面写的软件驱动。在driver.c文件中首先需要定义一个platform_driver结构体。然后去实现这个结构体中的各个成员变量。当driver.c和device.c匹配成功以后,会执行driver.c里面的probe函数。platform_driver这个结构体定义在include/linux/platform_device.h文件当中,结构体原型如下:

匹配过程和调用驱动中的probe函数后面会再说。
platform设备加载和卸载函数
1.platform设备加载函数:
函数原型:intIlatform_driver_registepr(struct platform_driver *driver)
函数作用:加载platform设备。
2. platform设备卸载函数:
函数原型:void platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *driver)
函数作用:卸载platform设备。
int my_probe(struct platform_device *)
{}int my_remove(struct platform_device *)
{}const struct platform_device_id my_id_table = {.name = "my_driver",
};static struct platform_driver my_driver = {.probe = my_probe,.remove = my_remove,.driver = {.name = "my_driver",.owner = THIS_MODULE,},.id_table = &my_id_table,
};int __init my_input_init(void)
{platform_driver_register(&my_driver);return ret;
}void __exit my_input_exit(void)
{platform_driver_unregister(&my_driver);
}注册平台驱动框架如上。
三种匹配方式, 名称匹配, id匹配, 设备树匹配。优先级由低到高。
- 设备与驱动的名称匹配



- 设备与驱动的ID匹配


- 设备树匹配


设备树匹配是不需要设备端的代码的, 由系统启动的时候解析设备树, 得到的device_node,满足条件的再转为平台设备。后面可能还会再出设备树, 设备模型相关的文章。
六、编写probe函数
驱动是要控制硬件的。但是平台总线模型对硬件的描述是在设备(device)中的。所以在驱动(driver)中,我们需要得到设备(device)中的硬件资源。当设备(device)和驱动(driver)匹配成功以后,会执行驱动(driver)中的probe函数,所以我们要在probe函数中拿到设备(device)中的硬件资源。所以,重点是怎么拿到这些硬件资源呢?
函数原型:extern struct resource *platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *,unsigned int,
unsigned int);
函数作用:获取device中的硬件资源。
函数参数:第一个参数platform_device结构体。第二个参数:资源的类型。第三个参数:索引号。资源处在同类资源的哪个位置上。同类资源指的是flags是一样的同类资源。

返回资源数组中的指定的哪一个的地址。
int my_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{if (dev == NULL){goto err_probe;}struct resource dev_source;dev_source = platform_get_resource(dev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0)if (dev_source == NULL) {printk("platform_get_resource failed\r\n");return -2;}/* use dev_source */err_probe:return -1;
}拿到resource结构体之后, 使用gpio, 内存, 中断都是有相应的函数的, 根据不同的功能去选择。
七、平台总线源码分析
先从注册设备端的源码入手。设备基类数据结构如下
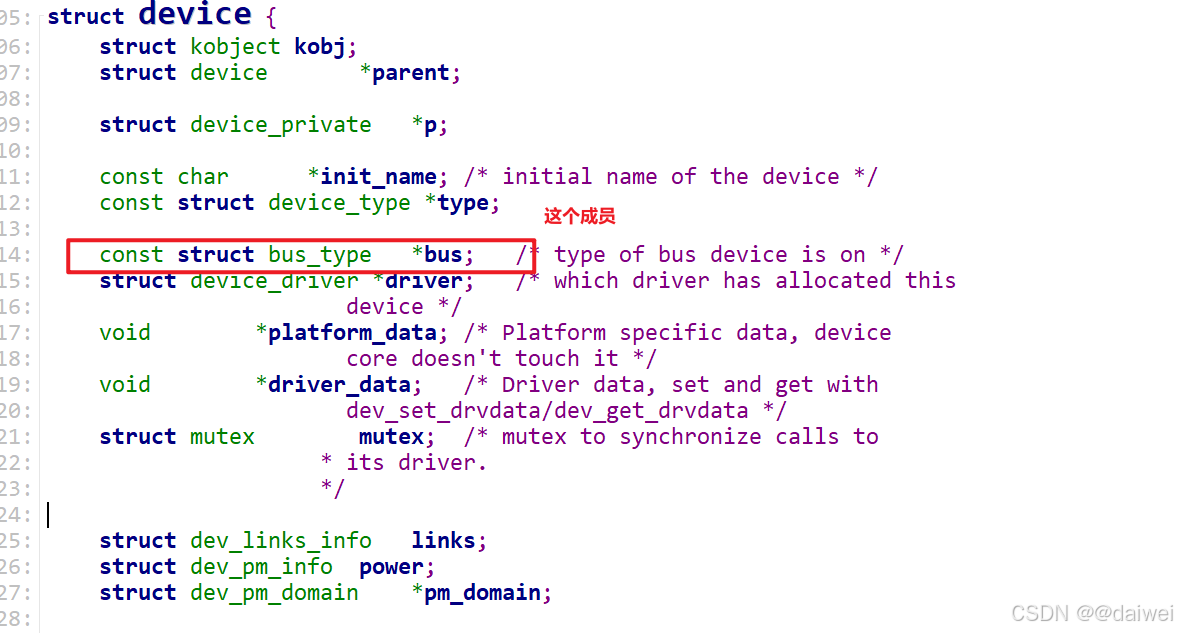
/*** struct device - The basic device structure* @parent: The device's "parent" device, the device to which it is attached.* In most cases, a parent device is some sort of bus or host* controller. If parent is NULL, the device, is a top-level device,* which is not usually what you want.* @p: Holds the private data of the driver core portions of the device.* See the comment of the struct device_private for detail.* @kobj: A top-level, abstract class from which other classes are derived.* @init_name: Initial name of the device.* @type: The type of device.* This identifies the device type and carries type-specific* information.* @mutex: Mutex to synchronize calls to its driver.* @bus: Type of bus device is on.* @driver: Which driver has allocated this* @platform_data: Platform data specific to the device.* Example: For devices on custom boards, as typical of embedded* and SOC based hardware, Linux often uses platform_data to point* to board-specific structures describing devices and how they* are wired. That can include what ports are available, chip* variants, which GPIO pins act in what additional roles, and so* on. This shrinks the "Board Support Packages" (BSPs) and* minimizes board-specific #ifdefs in drivers.* @driver_data: Private pointer for driver specific info.* @links: Links to suppliers and consumers of this device.* @power: For device power management.* See Documentation/driver-api/pm/devices.rst for details.* @pm_domain: Provide callbacks that are executed during system suspend,* hibernation, system resume and during runtime PM transitions* along with subsystem-level and driver-level callbacks.* @em_pd: device's energy model performance domain* @pins: For device pin management.* See Documentation/driver-api/pin-control.rst for details.* @msi: MSI related data* @numa_node: NUMA node this device is close to.* @dma_ops: DMA mapping operations for this device.* @dma_mask: Dma mask (if dma'ble device).* @coherent_dma_mask: Like dma_mask, but for alloc_coherent mapping as not all* hardware supports 64-bit addresses for consistent allocations* such descriptors.* @bus_dma_limit: Limit of an upstream bridge or bus which imposes a smaller* DMA limit than the device itself supports.* @dma_range_map: map for DMA memory ranges relative to that of RAM* @dma_parms: A low level driver may set these to teach IOMMU code about* segment limitations.* @dma_pools: Dma pools (if dma'ble device).* @dma_mem: Internal for coherent mem override.* @cma_area: Contiguous memory area for dma allocations* @dma_io_tlb_mem: Software IO TLB allocator. Not for driver use.* @dma_io_tlb_pools: List of transient swiotlb memory pools.* @dma_io_tlb_lock: Protects changes to the list of active pools.* @dma_uses_io_tlb: %true if device has used the software IO TLB.* @archdata: For arch-specific additions.* @of_node: Associated device tree node.* @fwnode: Associated device node supplied by platform firmware.* @devt: For creating the sysfs "dev".* @id: device instance* @devres_lock: Spinlock to protect the resource of the device.* @devres_head: The resources list of the device.* @knode_class: The node used to add the device to the class list.* @class: The class of the device.* @groups: Optional attribute groups.* @release: Callback to free the device after all references have* gone away. This should be set by the allocator of the* device (i.e. the bus driver that discovered the device).* @iommu_group: IOMMU group the device belongs to.* @iommu: Per device generic IOMMU runtime data* @physical_location: Describes physical location of the device connection* point in the system housing.* @removable: Whether the device can be removed from the system. This* should be set by the subsystem / bus driver that discovered* the device.** @offline_disabled: If set, the device is permanently online.* @offline: Set after successful invocation of bus type's .offline().* @of_node_reused: Set if the device-tree node is shared with an ancestor* device.* @state_synced: The hardware state of this device has been synced to match* the software state of this device by calling the driver/bus* sync_state() callback.* @can_match: The device has matched with a driver at least once or it is in* a bus (like AMBA) which can't check for matching drivers until* other devices probe successfully.* @dma_coherent: this particular device is dma coherent, even if the* architecture supports non-coherent devices.* @dma_ops_bypass: If set to %true then the dma_ops are bypassed for the* streaming DMA operations (->map_* / ->unmap_* / ->sync_*),* and optionall (if the coherent mask is large enough) also* for dma allocations. This flag is managed by the dma ops* instance from ->dma_supported.** At the lowest level, every device in a Linux system is represented by an* instance of struct device. The device structure contains the information* that the device model core needs to model the system. Most subsystems,* however, track additional information about the devices they host. As a* result, it is rare for devices to be represented by bare device structures;* instead, that structure, like kobject structures, is usually embedded within* a higher-level representation of the device.*/
struct device {struct kobject kobj;struct device *parent;struct device_private *p;const char *init_name; /* initial name of the device */const struct device_type *type;const struct bus_type *bus; /* type of bus device is on */struct device_driver *driver; /* which driver has allocated thisdevice */void *platform_data; /* Platform specific data, devicecore doesn't touch it */void *driver_data; /* Driver data, set and get withdev_set_drvdata/dev_get_drvdata */struct mutex mutex; /* mutex to synchronize calls to* its driver.*/struct dev_links_info links;struct dev_pm_info power;struct dev_pm_domain *pm_domain;#ifdef CONFIG_ENERGY_MODELstruct em_perf_domain *em_pd;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_PINCTRLstruct dev_pin_info *pins;
#endifstruct dev_msi_info msi;
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_OPSconst struct dma_map_ops *dma_ops;
#endifu64 *dma_mask; /* dma mask (if dma'able device) */u64 coherent_dma_mask;/* Like dma_mask, but foralloc_coherent mappings asnot all hardware supports64 bit addresses for consistentallocations such descriptors. */u64 bus_dma_limit; /* upstream dma constraint */const struct bus_dma_region *dma_range_map;struct device_dma_parameters *dma_parms;struct list_head dma_pools; /* dma pools (if dma'ble) */#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_DECLARE_COHERENTstruct dma_coherent_mem *dma_mem; /* internal for coherent memoverride */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_CMAstruct cma *cma_area; /* contiguous memory area for dmaallocations */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SWIOTLBstruct io_tlb_mem *dma_io_tlb_mem;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SWIOTLB_DYNAMICstruct list_head dma_io_tlb_pools;spinlock_t dma_io_tlb_lock;bool dma_uses_io_tlb;
#endif/* arch specific additions */struct dev_archdata archdata;struct device_node *of_node; /* associated device tree node */struct fwnode_handle *fwnode; /* firmware device node */#ifdef CONFIG_NUMAint numa_node; /* NUMA node this device is close to */
#endifdev_t devt; /* dev_t, creates the sysfs "dev" */u32 id; /* device instance */spinlock_t devres_lock;struct list_head devres_head;const struct class *class;const struct attribute_group **groups; /* optional groups */void (*release)(struct device *dev);struct iommu_group *iommu_group;struct dev_iommu *iommu;struct device_physical_location *physical_location;enum device_removable removable;bool offline_disabled:1;bool offline:1;bool of_node_reused:1;bool state_synced:1;bool can_match:1;
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_DEVICE) || \defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_CPU) || \defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_CPU_ALL)bool dma_coherent:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_OPS_BYPASSbool dma_ops_bypass : 1;
#endif
};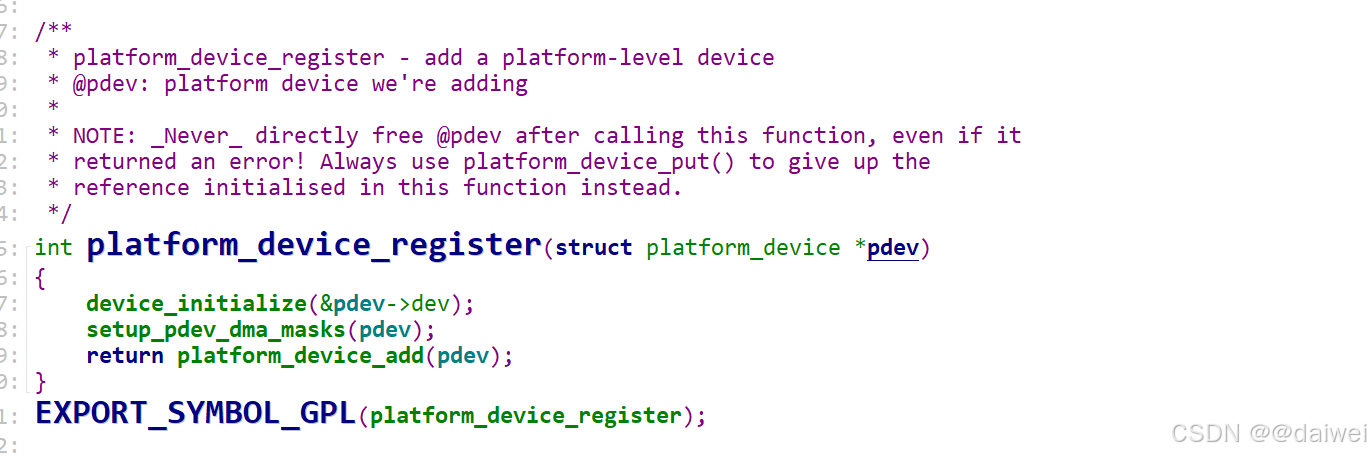
注册平台设备调用了三个函数, 按照顺序查看。
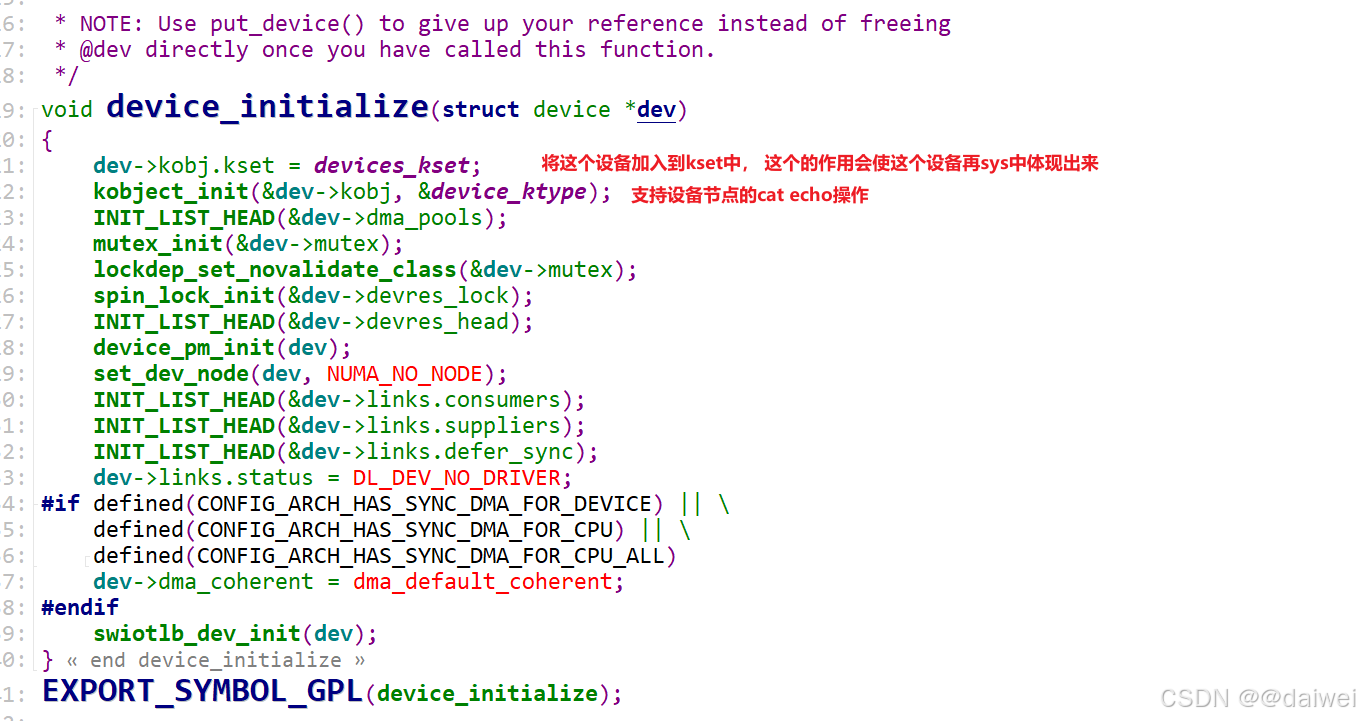
这里涉及到了很多的sys, 也就是设备模型的东西, 后面单独出文章讲讲这个sys, 也随便我自己梳理一下这个sys设备模型这块的东西。重点还是看这个函数platform_device_add, 文件路径drivers\base\platform.c
/*** platform_device_add - 将平台设备添加到设备层次结构中* @pdev: 要添加的平台设备** 这是 platform_device_register() 的第二部分,可以单独调用,但前提是 pdev 是通过 platform_device_alloc() 分配的。*/
int platform_device_add(struct platform_device *pdev)
{u32 i; // 用于遍历资源的索引int ret; // 返回值if (!pdev)return -EINVAL; // 如果 pdev 为空,返回无效参数错误if (!pdev->dev.parent)pdev->dev.parent = &platform_bus; // 设置设备的父设备为 platform_buspdev->dev.bus = &platform_bus_type; // 设置设备的总线类型为 platform_bus_type// 根据设备 ID 设置设备名称switch (pdev->id) {default:dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d", pdev->name, pdev->id); // 设置设备名称为 "name.id"break;case PLATFORM_DEVID_NONE:dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s", pdev->name); // 设置设备名称为 "name"break;case PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO:/** 自动分配的设备 ID。我们将其标记为自动分配,以便记住它需要被释放,并附加一个后缀* 以避免与显式 ID 的命名空间冲突。*/ret = ida_alloc(&platform_devid_ida, GFP_KERNEL); // 分配一个新的设备 IDif (ret < 0)goto err_out; // 如果分配失败,跳转到错误处理pdev->id = ret; // 设置设备 IDpdev->id_auto = true; // 标记为自动分配的 IDdev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d.auto", pdev->name, pdev->id); // 设置设备名称为 "name.id.auto"break;}// 遍历设备的资源并插入到资源树中for (i = 0; i < pdev->num_resources; i++) {struct resource *p, *r = &pdev->resource[i]; // 获取当前资源if (r->name == NULL)r->name = dev_name(&pdev->dev); // 如果资源名称为空,设置为设备名称p = r->parent; // 获取资源的父资源if (!p) {if (resource_type(r) == IORESOURCE_MEM)p = &iomem_resource; // 如果是内存资源,父资源为 iomem_resourceelse if (resource_type(r) == IORESOURCE_IO)p = &ioport_resource; // 如果是 I/O 资源,父资源为 ioport_resource}if (p) {ret = insert_resource(p, r); // 将资源插入到资源树中if (ret) {dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to claim resource %d: %pR\n", i, r); // 如果插入失败,记录错误goto failed; // 跳转到错误处理}}}pr_debug("Registering platform device '%s'. Parent at %s\n",dev_name(&pdev->dev), dev_name(pdev->dev.parent)); // 打印调试信息ret = device_add(&pdev->dev); // 将设备添加到设备层次结构中if (ret == 0)return ret; // 如果成功,返回 0failed:if (pdev->id_auto) {ida_free(&platform_devid_ida, pdev->id); // 如果 ID 是自动分配的,释放 IDpdev->id = PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO; // 重置 ID}// 释放所有已分配的资源while (i--) {struct resource *r = &pdev->resource[i];if (r->parent)release_resource(r); // 释放资源}err_out:return ret; // 返回错误码
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_device_add); // 导出符号,使其可以被 GPL 模块使用 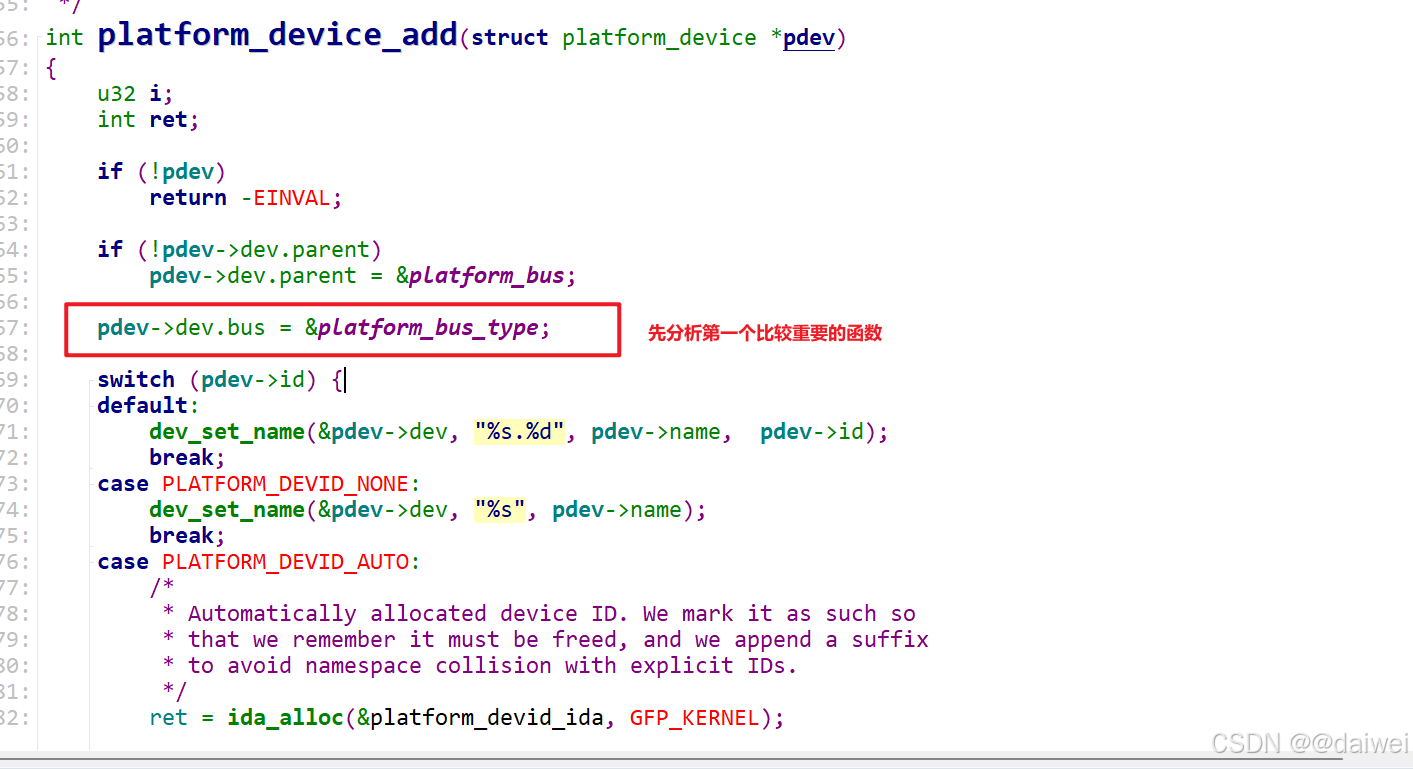
数据结构原型:
/*** struct bus_type - The bus type of the device** @name: The name of the bus.* @dev_name: Used for subsystems to enumerate devices like ("foo%u", dev->id).* @bus_groups: Default attributes of the bus.* @dev_groups: Default attributes of the devices on the bus.* @drv_groups: Default attributes of the device drivers on the bus.* @match: Called, perhaps multiple times, whenever a new device or driver* is added for this bus. It should return a positive value if the* given device can be handled by the given driver and zero* otherwise. It may also return error code if determining that* the driver supports the device is not possible. In case of* -EPROBE_DEFER it will queue the device for deferred probing.* @uevent: Called when a device is added, removed, or a few other things* that generate uevents to add the environment variables.* @probe: Called when a new device or driver add to this bus, and callback* the specific driver's probe to initial the matched device.* @sync_state: Called to sync device state to software state after all the* state tracking consumers linked to this device (present at* the time of late_initcall) have successfully bound to a* driver. If the device has no consumers, this function will* be called at late_initcall_sync level. If the device has* consumers that are never bound to a driver, this function* will never get called until they do.* @remove: Called when a device removed from this bus.* @shutdown: Called at shut-down time to quiesce the device.** @online: Called to put the device back online (after offlining it).* @offline: Called to put the device offline for hot-removal. May fail.** @suspend: Called when a device on this bus wants to go to sleep mode.* @resume: Called to bring a device on this bus out of sleep mode.* @num_vf: Called to find out how many virtual functions a device on this* bus supports.* @dma_configure: Called to setup DMA configuration on a device on* this bus.* @dma_cleanup: Called to cleanup DMA configuration on a device on* this bus.* @pm: Power management operations of this bus, callback the specific* device driver's pm-ops.* @iommu_ops: IOMMU specific operations for this bus, used to attach IOMMU* driver implementations to a bus and allow the driver to do* bus-specific setup* @need_parent_lock: When probing or removing a device on this bus, the* device core should lock the device's parent.** A bus is a channel between the processor and one or more devices. For the* purposes of the device model, all devices are connected via a bus, even if* it is an internal, virtual, "platform" bus. Buses can plug into each other.* A USB controller is usually a PCI device, for example. The device model* represents the actual connections between buses and the devices they control.* A bus is represented by the bus_type structure. It contains the name, the* default attributes, the bus' methods, PM operations, and the driver core's* private data.*/
struct bus_type {const char *name;const char *dev_name;const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;const struct attribute_group **drv_groups;int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);int (*uevent)(const struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);int (*probe)(struct device *dev);void (*sync_state)(struct device *dev);void (*remove)(struct device *dev);void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);int (*online)(struct device *dev);int (*offline)(struct device *dev);int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);int (*resume)(struct device *dev);int (*num_vf)(struct device *dev);int (*dma_configure)(struct device *dev);void (*dma_cleanup)(struct device *dev);const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;bool need_parent_lock;
};

后面设备和驱动匹配的时候就是调用了这些当中的一些函数。
调用过程关系
platform_device_register
platform_device_add
device_add
bus_probe_device
device_initial_probe
__device_attach
__device_attach_driver
driver_probe_device
__driver_probe_device
really_probe
在really_probe函数中调用找到的匹配上的驱动中的probe函数。这里看了驱动端的platform_driver_register函数的实现, 发现和设备端的实现差不多。直接上实现的原理
原理分析:
维护了两条链表,一个是设备的, 一个是驱动的, 当注册设备的时候, 调用总线的匹配函数, 这个匹配函数会根据规则匹配, 用当前注册的设备和驱动链表中的一 一做匹配, 匹配上之后, 调用驱动中的probe函数, 注册驱动也是一样的道理。
相关文章:

平台总线---深入分析
阅读引言:本文会从平台总线的介绍,注册平台设备和驱动, 源码分析, 总结五个部分展开, 源码分析platform放在了最后面。 目录 一、平台总线介绍 二、平台总线如何使用 三、平台总线是如何工作的 四、注册platform设…...

pyTorch框架:模型的子类写法--改进版二分类问题
目录 1.导包 2.加载数据 3.数据的特征工程 4.pytorch中最常用的一种创建模型的方式--子类写法 1.导包 import torch import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt2.加载数据 data pd.read_csv(./dataset/HR.csv)data.head() #查看数据的前…...

【python中级】解压whl文件内容
【python中级】解压whl文件内容 1.背景2.解压1.背景 【python中级】关于whl文件的说明 https://blog.csdn.net/jn10010537/article/details/146979236 补充以上博客: 在 旧版 setuptools 中(< v58),如果想生成 .whl,必须先pip install 安装 wheel 三方包! pip inst…...

【USRP】srsRAN 开源 4G 软件无线电套件
srsRAN 是SRS开发的开源 4G 软件无线电套件。 srsRAN套件包括: srsUE - 具有原型 5G 功能的全栈 SDR 4G UE 应用程序srsENB - 全栈 SDR 4G eNodeB 应用程序srsEPC——具有 MME、HSS 和 S/P-GW 的轻量级 4G 核心网络实现 安装系统 Ubuntu 20.04 USRP B210 sudo …...
_30)
LeetCode算法题(Go语言实现)_30
题目 给定单链表的头节点 head ,将所有索引为奇数的节点和索引为偶数的节点分别组合在一起,然后返回重新排序的列表。 第一个节点的索引被认为是 奇数 , 第二个节点的索引为 偶数 ,以此类推。 请注意,偶数组和奇数组内…...

生信入门:专栏概要与内容目录
文章目录 生信入门📚 核心内容模块基础概念入门序列联配算法高级算法与应用理论基础与数学方法基因组分析 生信入门 🔥 专栏简介 | 生信算法与实践指南 开启生物信息学的学习之旅 🌟 为什么订阅本专栏? 循序渐进:从生…...

Matplotlib:数据可视化的艺术与科学
引言:让数据开口说话 在数据分析与机器学习领域,可视化是理解数据的重要桥梁。Matplotlib 作为 Python 最流行的绘图库,提供了从简单折线图到复杂 3D 图表的完整解决方案。本文将通过实际案例,带您从基础绘图到高级定制全面掌握 …...

线程共享数据所带来的安全性问题
笔记 import threading from threading import Thread import time tickte50 # 代表的是50张票def sale_ticket():global tickte# 每个排队窗口假设有100人for i in range(100): # 每个线程要执行100次循环if tickte>0:print(f{threading.current_thread().name}正在出售第…...

Redis核心机制-缓存、分布式锁
目录 缓存 缓存更新策略 定期生成 实时生成 缓存问题 缓存预热(Cache preheating) 缓存穿透(Cache penetration) 缓存雪崩(Cache avalanche) 缓存击穿(Cache breakdown) 分…...

Node.js中间件的5个注意事项
目录 1. 目录结构 2. 代码实现 注意事项 1:必须调用 next() 注意事项 2:中间件的执行顺序很重要 注意事项 3:局部中间件的使用 注意事项 4:统一处理 404 注意事项 5:使用错误处理中间件 3. 总结 在Node.js的Ex…...

软件学报 2024年 区块链论文 录用汇总 附pdf下载
Year:2024 1 Title: 带有预验证机制的区块链动态共识算法 Authors: Key words: 区块链;混合共识;预验证机制;动态共识;委员会腐败 Abstract: 委员会共识和混合共识通过选举委员会来代替全网节点完成区块验证, 可有效加快共识速度, 提高吞吐量, 但恶意攻击和收…...
)
从开发到上线:基于 Linux 云服务器的前后端分离项目部署实践(Vue + Node.js)
明白了,这次我们完全聚焦技术内容本身,不带明显广告语言,不插入链接,只在文末一个不显眼的地方轻描淡写提到“服务器用的是 zovps.com 的一台基础云主机”,整体文章保证原创、高质量、易审核、易分发,长度控…...

FastAPI-Cache2: 高效Python缓存库
FastAPI-Cache2是一个强大而灵活的Python缓存库,专为提升应用性能而设计。虽然其名称暗示与FastAPI框架的紧密集成,但实际上它可以在任何Python项目中使用,为开发者提供简单而高效的缓存解决方案。 在现代应用开发中,性能优化至关…...

提高:图论:强连通分量 图的遍历
时间限制 : 1 秒 内存限制 : 128 MB 给出 NN 个点,MM 条边的有向图,对于每个点 vv,求 A(v)A(v) 表示从点 vv 出发,能到达的编号最大的点。 输入 第 11 行 22 个整数 N,MN,M,表示点数和边数。 接下来 MM 行&#x…...

RabbitMQ高级特性2
RabbitMQ高级特性2 一.TTL1.设置消息的TTL2.设置队列的过期时间 二.死信队列1.死信2.代码实现3.消息被拒绝的死信超出队列长度时的死信死信队列的应用场景 三.延迟队列1.概念2.应用场景3.代码实现延迟队列插件安装和配置代码 4.总结 四.事务1.未采用事务2.采用事务 五.消息分发…...

基于FPGA的特定序列检测器verilog实现,包含testbench和开发板硬件测试
目录 1.课题概述 2.系统测试效果 3.核心程序与模型 4.系统原理简介 5.完整工程文件 1.课题概述 本课题采用基于伪码匹配相关峰检测的方式实现基于FPGA的特定序列检测器verilog实现,包含testbench和开发板硬件测试。 2.系统测试效果 仿真测试 当检测到序列的时候…...

【大数据知识】Flink分布式流处理和批处理框架
Flink分布式流处理和批处理框架 概述Flink入门介绍**1. Flink是什么?****2. 核心特性****3. 核心组件****4. 应用场景** Flink底层实现原理详细说明**1. 分布式架构****2. 流处理模型****3. 状态管理****4. 容错机制****5. 网络通信与数据传输****6. 资源管理与扩展…...

Java面试黄金宝典33
1. 什么是存取控制、 触发器、 存储过程 、 游标 存取控制 定义:存取控制是数据库管理系统(DBMS)为保障数据安全性与完整性,对不同用户访问数据库对象(如表、视图等)的权限加以管理的机制。它借助定义用户…...

实战解析:基于AWS Serverless架构的高并发微服务设计与优化
随着云计算进入深水区,Serverless架构正在重塑现代微服务的设计范式。本文将以电商秒杀系统为场景,基于AWS Serverless服务构建高可用架构,并深入探讨性能优化方案。 一、架构设计解析 我们采用分层架构设计,核心组件包括&#…...

Muduo网络库介绍
1.Reactor介绍 1.回调函数 **回调(Callback)**是一种编程技术,允许将一个函数作为参数传递给另一个函数,并在适当的时候调用该函数 1.工作原理 定义回调函数 注册回调函数 触发回调 2.优点 异步编程 回调函数允许在事件发生时…...
)
Cribl 导入文件来检查pipeline 的设定规则(eval 等)
Cribl 导入文件来检查pipeline 的设定规则(eval 等) 从这个页面先下载,或者copy 内容来创建pipeline: Reducing Windows XML Events | Cribl Docs...

2360. 图中的最长环
2360. 图中的最长环 题目链接:2360. 图中的最长环 代码如下: //参考链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-cycle-in-a-graph/solutions/1710828/nei-xiang-ji-huan-shu-zhao-huan-li-yong-pmqmr class Solution { public:int longest…...
:神经网络的学习)
深度学习入门(三):神经网络的学习
文章目录 前言人类思考 VS 机器学习 VS 深度学习基础术语损失函数常用的损失函数均方误差MSE(Mean Square Error)交叉熵误差(Cross Entropy Error)mini-batch学习 为何要设定损失函数数值微分神经网络学习算法的实现两层神经网络的…...

Python 推导式:简洁高效的数据生成方式
为什么需要推导式? 在Python编程中,我们经常需要对数据进行各种转换和过滤操作。传统的方法是使用循环结构,但这往往会导致代码冗长且不够直观。Python推导式(Comprehensions)应运而生,它提供了一种简洁、…...

HTML5+CSS3+JS小实例:带滑动指示器的导航图标
实例:带滑动指示器的导航图标 技术栈:HTML+CSS+JS 效果: 源码: 【HTML】 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, ini…...

一周学会Pandas2 Python数据处理与分析-Jupyter Notebook安装
锋哥原创的Pandas2 Python数据处理与分析 视频教程: 2025版 Pandas2 Python数据处理与分析 视频教程(无废话版) 玩命更新中~_哔哩哔哩_bilibili Jupyter (Project Jupyter | Home)项目是一个非营利性开源项目,于2014年由IPython项目中诞生…...

FPGA状态机思想实现流水灯及HDLBits学习
目录 第一章 在DE2-115上用状态机思想实现LED流水灯1.1 状态机设计思路1.2 Verilog代码实现1.3. 仿真测试代码1.4 编译代码与仿真 第二章 CPLD和FPGA芯片的主要技术区别是什么?它们各适用于什么场合?2.1 主要技术区别2.2 适用场合 第三章 HDLBits学习3.1…...

【教程】Windows下 Xshell 连接跳板机和开发机
需求 使用远程连接工具 Xshell 连接跳板机,再从跳板机连接开发机,用户登陆方式为使用密钥。 方法 首先,建立一个会话,用于配置跳板机信息和开发机转跳信息: 在【连接】页面,给跳板机取个名字,…...

Java导出excel,表格插入pdf附件,以及实现过程中遇见的坑
1.不能使用XSSFWorkbook,必须使用HSSFWorkbook,否则导出excel后,不显示插入的图标和内容,如果是读取的已有的excel模板,必须保证excel的格式是xls,如果把xlsx通过重命名的方式改为xls,是不生效的,后面执行下…...

神马系统8.5搭建过程,附源码数据库
项目介绍 神马系统是多年来流行的一款电视端应用,历经多年的发展,在稳定性和易用性方面都比较友好。 十多年前当家里的第一台智能电视买回家,就泡在某论坛,找了很多APP安装在电视上,其中这个神马系统就是用得很久的一…...

cesium 材质 与 交互 以及 性能相关介绍
文章目录 cesium 材质 与 交互 以及 性能相关介绍1. Cesium 材质与着色器简介2. 具体实例应用核心代码及解释3. 代码解释 Cesium 交互1. 常见交互和事件类型2. 示例代码及解释3. 代码解释 cesium 性能优化数据加载与管理渲染优化相机与场景管理代码优化服务器端优化 案例分享1.…...

指令补充+样式绑定+计算属性+监听器
一、指令补充 1. 指令修饰符 1. 作用: 借助指令修饰符, 可以让指令更加强大 2. 分类: 1> 按键修饰符: 用来检测用户的按键, 配合键盘事件使用. keydown 和 keyup 语法: keydown.enter/v-on:keydown.enter 表示当enter按下的时候触发 keyup.enter/v-on:keyup.enter 表示当…...
,源码可白嫖!)
基于Android的病虫害防治技术系统(源码+lw+部署文档+讲解),源码可白嫖!
摘要 基于Android的病虫害防治技术系统设计的目的是为用户提供一个病虫害防治技术管理的平台。与PC端应用程序相比,病虫害防治技术管理的设计主要面向于广大用户,旨在为用户提供一个查看科普内容,进行病虫识别、发帖交流的平台。 基于Androi…...

ffmpeg 使用不同编码器编码hevc的速度
1.核显uhd630 编码器hevc_qsv ffmpeg版本2024-03-14 2.73X 转码完成后大小 971mb 2.1680V4 编码器 libx265 ffmpeg版本2025-05-07 1.42x 转码完成后大小 176mb 3.RX588 编码器hevc_amf ffmpeg版本2024-03-14 转码完成后大小 376MB 4.1680v4dg1rx584 编码器hevc_amf ffm…...

【硬件模块】数码管模块
一位数码管 共阳极数码管:8个LED共用一个阳极 数字编码00xC010xF920xA430xB040x9950x9260x8270xF880x8090x90A0x88B0x83C0xC6D0xA1E0x86F0x8E 共阴极数码管:8个LED共用一个阴极 数字编码00x3F10x0620x5B30x4F40x6650x6D60x7D70x0780x7F90x6FA0x77B0x7…...
)
NO.64十六届蓝桥杯备战|基础算法-简单贪心|货仓选址|最大子段和|纪念品分组|排座椅|矩阵消除(C++)
贪⼼算法是两极分化很严重的算法。简单的问题会让你觉得理所应当,难⼀点的问题会让你怀疑⼈⽣ 什么是贪⼼算法? 贪⼼算法,或者说是贪⼼策略:企图⽤局部最优找出全局最优。 把解决问题的过程分成若⼲步;解决每⼀步时…...

ubuntu22.04LTS设置中文输入法
打开搜狗网址直接下载软件,软件下载完成后,会弹出安装教程说明书。 网址:搜狗输入法linux-首页搜狗输入法for linux—支持全拼、简拼、模糊音、云输入、皮肤、中英混输https://shurufa.sogou.com/linux...

基于YOLOv8的热力图生成与可视化-支持自定义模型与置信度阈值的多维度分析
目标检测是计算机视觉领域的重要研究方向,而YOLO(You Only Look Once)系列算法因其高效性和准确性成为该领域的代表性方法。YOLOv8作为YOLO系列的最新版本,在目标检测任务中表现出色。然而,传统的目标检测结果通常以边…...

常见设计系统清单
机构设计系统toB/toC网站GoogleMaterial DesignCm3.material.ioIBM CarbonDesign SystemBcarbondesignsystem.comSalesforceLightning Design SystemBlightningdesignsystem.comMicrosoftFluent Design SystemCfluent2.microsoft.design阿里Ant DesignCant.designSAPFiori Desi…...
)
React编程高级主题:错误处理(Error Handling)
文章目录 **5.2 错误处理(Error Handling)概述****5.2.1 onErrorReturn / onErrorResume(错误回退)****1. onErrorReturn:提供默认值****2. onErrorResume:切换备用数据流** **5.2.2 retry / retryWhen&…...

【设计模式】代理模式
简介 假设你在网上购物时,快递员无法直接将包裹送到你手中(比如你不在家)。 代理模式的解决方案是: 快递员将包裹交给小区代收点(代理),代收点代替你控制和管理包裹的访问。 代收点可以添加额外…...

局域网:电脑或移动设备作为主机实现局域网访问
电脑作为主机 1. 启用电脑的网络发现、SMB功能 2. 将访问设备开启WIFI或热点,用此电脑连接;或多台设备连接到同一WIFI 3. 此电脑打开命令行窗口,查看电脑本地的IP地址 Win系统:输入"ipconfig",回车后如图 4.…...

图论的基础
E - Replace(判环,破环成链) #include <bits/stdc.h> #include <atcoder/dsu>using namespace std; using namespace atcoder;const int C 26;int main() {int n;cin >> n;string s, t;cin >> s >> t;if (s …...

Jetpack Compose CompositionLocal 深入解析:局部参数透传实践
Jetpack Compose CompositionLocal 深入解析:局部参数透传实践 在 Jetpack Compose 中,如何优雅地在组件之间传递数据,而不需要层层传参? CompositionLocal 就是为了解决这个问题的! 1. 什么是 CompositionLocal&#…...

第十五届蓝桥杯大赛软件赛省赛Python 大学 C 组:3.数字诗意
题目1 数字诗意 在诗人的眼中,数字是生活的韵律,也是诗意的表达。 小蓝,当代顶级诗人与数学家,被赋予了”数学诗人”的美誉。他擅长将冰冷的数字与抽象的诗意相融合,并用优雅的文字将数学之美展现于纸上。 某日&…...
对比>)
Oracle数据库数据编程SQL<8 文本编辑器Notepad++和UltraEdit(UE)对比>
首先,用户界面方面。Notepad是开源的,界面看起来比较简洁,可能更适合喜欢轻量级工具的用户。而UltraEdit作为商业软件,界面可能更现代化,功能布局更复杂一些。不过,UltraEdit支持更多的主题和自定义选项&am…...

P12013 [Ynoi April Fool‘s Round 2025] 牢夸 Solution
Description 给定序列 a ( a 1 , a 2 , ⋯ , a n ) a(a_1,a_2,\cdots,a_n) a(a1,a2,⋯,an),有 m m m 个操作分两种: add ( l , r , k ) \operatorname{add}(l,r,k) add(l,r,k):对每个 i ∈ [ l , r ] i\in[l,r] i∈[l,r] 执行 …...

PostgreSQL LIKE 操作符详解
PostgreSQL LIKE 操作符详解 引言 在数据库查询中,LIKE 操作符是一种非常常用的字符串匹配工具。它可以帮助我们实现模糊查询,从而提高查询的灵活性。本文将详细介绍 PostgreSQL 中的 LIKE 操作符,包括其语法、使用方法以及一些注意事项。 LIKE 操作符语法 LIKE 操作符通…...

【前端】【Nuxt3】Nuxt3的生命周期
路由导航和中间件执行顺序 路由导航开始 中间件执行顺序: 全局中间件(middleware/*.global.js)布局中间件(在definePageMeta中定义的布局级中间件)页面中间件(在definePageMeta中定义的页面级中间件&#…...

热更新简介+xLua基础调用
什么是冷更新 开发者将测试好的代码,发布到应用商店的审核平台,平台方会进行稳定性及性能测试。测试成功后,用户即可在AppStore看到应用的更新信息,用户点击应用更新后,需要先关闭应用,再进行更新。 什么是…...
