三、The C in C++
第三章主要讲解了 C++ 中继承自 C 语言的核心元素,包括函数创建、执行控制、操作符、数据类型、作用域、存储指示、复合类型创建等。
3.1 创建函数(Creating Functions)
- C++允许函数重载,同名的函数可以根据参数类型和数量区分:
int add(int x, int y, int z);
int add(float,float,float);
void add();
- 函数可放入自己的函数库,构成.h 和 .lib 文件,方便重复使用和分布。
3.2 控制程序的执行流程(Controlling execution)
- 分支:if-else,switch-case
- 循环类型:while,do-while,for
- 特殊操作:break 中断循环,continue 跳过本轮继续
- 递归:函数自己调用自己
3.3操作符
- 一元操作符:++,–,,,&
- 二元操作符:+ - * / % = == != && || << >>
- 其他:?: 条件操作符,sizeof 等
- 进行计算时应使用括号明确进体顺序,避免误解
3.4 数据类型简介
基本类型:bool, char, int, float, double, void
指针:用于存放地址,需指明指向的类型
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int dog,cat,bird;
void f(int pet) {cout << "pet id number:" << pey << endl;}
void main(){int i,j;cout << "f(): " << &f << endl;//produce the addresscout << "dog: " << &dog << endl;cout << "cat: " << &cat << endl;cout << "bird: " << &bird << endl;cout << "i: " << &i << endl;cout << "j: " << &j << endl;int *p = new int;cout << "p: " << &p << endl;cout << "&(*p) :" << &(*p) << endl;//cout << "&(*p)" << p << endl delet p;
}
output:

由此可见
f()的地址在代码段/文本段,属于静态分配
dog,cat,bird,全局变量地址,地址相邻,分配在静态区(BSS段)
i、j, 局部变量,地址较低,且和全局变量区分明显,属于栈区,且高地址向低地址增长
&p , 局部变量int * p本身的地址,也是栈区
&(_p) , 动态分配的int 类型变量地址(通过*_new int),属于堆区。
引用:变量的别名,必须初始化,不可重新指向
int a=3,b=5;
int& m = a;//OK
int& m; // error
int& m = b;//ok
int&k = m;
int n = m;
int*p = &m;
int*& ref = p;
m = m+5
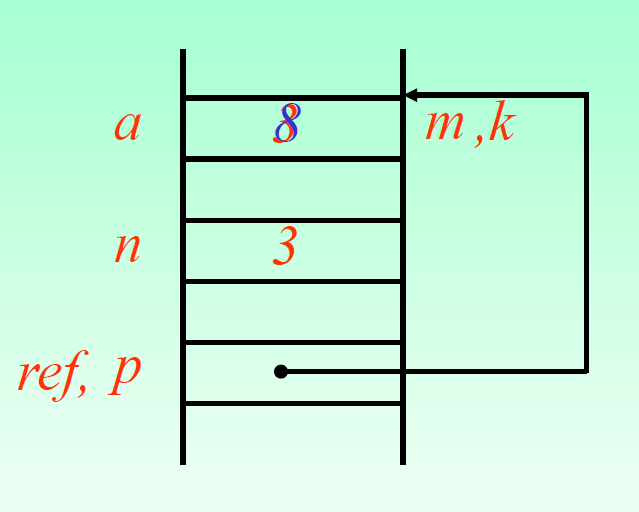
引用仅仅只是一个别名,就像m,k它们和a指向同一个位置,占用同一个内存
参数传递:分为值传递、地址传递、引用传递
int i = 10;
int *p = &i;
void* vp = p;//OK
int *ip = vp;//error
其他指针赋值给void*,但是不可以void*赋值给其他型
比较Argument Passing(Value,pointer,reference)
Pass by value
//C03:PassByValue.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void f(int a){cout << "a=" << a << endl;a = 5;cout << "a=" << a << endl;
}
void main(){int x = 47;cout << "x=" << x << endl;f(x);cout << "x=" << x << endl;
}
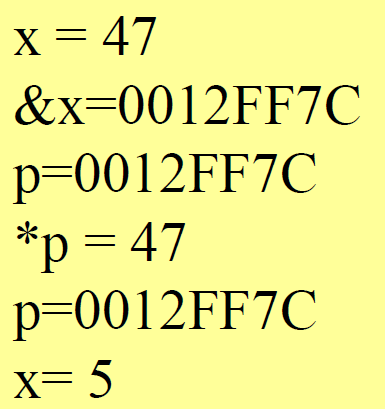
Pass by address
//C03:PassAddress.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void f(int *p){cout << "p=" << p << endl;cout << "*p=" << *p << endl;*p = 5;cout << "p=" << p << endl;
}
void main(){int x = 47;cout << "x=" << x << endl;cout << "&x=" << &x << endl;f(x);cout << "x=" << x << endl;
}
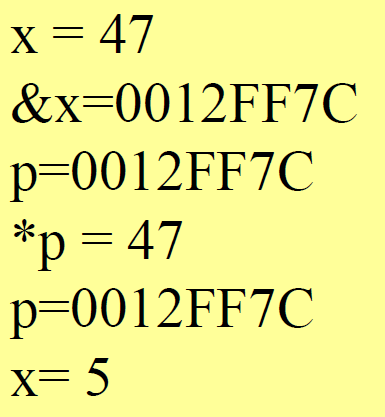
Pass reference
//C03:PassReference.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void f(int& a){cout << "a=" << a << endl;a = 5;cout << "a=" << a << endl;
}
void main(){int x = 47;cout << "x=" << x << endl;f(x);cout << "x=" << x << endl;
}

比较swap1(Value),swap2(address),swap3(reference)
Passing by Value
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap1(int x,int y){int temp;temp = x;x = y;y = temp;cout << "x=" << x << "," << "y=" << y << endl;
}
void main(){int a(5),b(9);swap1(a,b)//swap1(5,9);ok?cout << "a:" << a << "," << "b:" << b << endl;
}

问题swap1(5,9);ok?
OK。在 C++ 中,函数参数如果是值传递(pass by value),你完全可以传入常量字面值(如 5, 9),因为:
int x,int y是 值传递:函数内会把参数值拷贝一份到局部变量中;swap1(5, 9)等价于:x = 5; y = 9;—— 合法;- 虽然
x、y在函数中交换了,但这些交换并不会影响外部实参。
Passing by address
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap2(int* x,int* y){int temp;temp = *x;*x = *y;*y = temp;cout << "X = " << *x << "," << "y=" << *y << endl;
}
int main(){int a(5),b(9);swap2(&a,&b);//swap2(&5,&9);?cout << "a=" << a << "," << "b:" << b << endl;return 0;
}
output:

问题swap2(5,9);ok?
不OK。 函数参数是两个 int,也就是指向整型的指针,因此必须传入 **地址(address)。 然而 **5 和 9 是整型字面值(int),不是地址。编译器无法把 int 自动转换成 int(除非你非常暴力地强制类型转换)
Passing by reference
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap3(int& x,int& y){int temp;temp = x;x = y;y = temp;cout << "x=" << x << "," << "y=" << y << endl;
}
int main(){int a(5),b(9);swap3(a,b);//swap3(5,9);?cout << "a=" << a << "," << "a=" << a << endl;
}
output

问题swap3(5,9);ok?
不OK。这是引用传递(pass by reference),也就是说:
- 必须传入变量,因为函数参数会变成这些变量的别名(reference);
5和9是常量值,不是变量,不能作为引用参数;- 引用必须引用一个 具名对象(L-value),但
5、9是 R-value(右值),没有地址可引用;
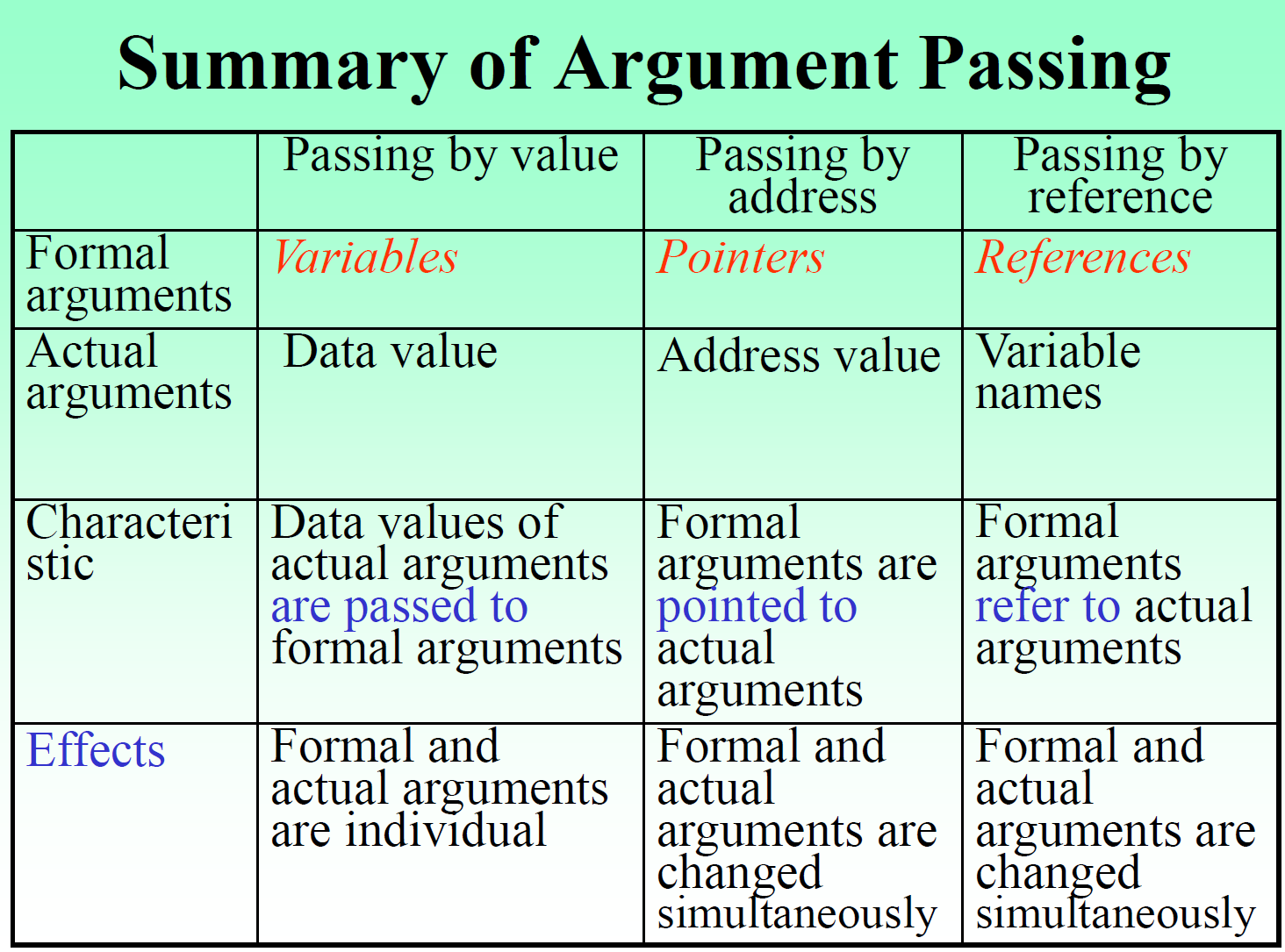
Summary of Argument Passing
3.5 作用域(Scoping)
3.5.1变量只能在其归属作用域内进行操作
void main(){int scp1;//scp1 visible here{ //scp1 still visible hereint scp2;//scp2 visible here{//scp1 & scp2 still visible hereint scp3;//scp1,scp2&scp3 visible here}//<<--scp3 destoryed here//scp3 not available here//scp1 & scp2 still visible here}//<<--scp2 destoryed here//scp3 & scp3 not available here
}//<<--scp1 destoryed here
- C++ allows you to define variable anywhere in a scope,so you can define a variable right before you use it
- It reduces the errors you get from being forced to jump back and forth within a scope
- 大括号定义一个新作用域
- C++ 允许在任意作用域内定义变量,更加灵活
3.6存储分配指示(Specifying storage allocation)
3.6.1 全局变量(Global variables)
- Global variables are defined outside all function bodies and are available to all parts of program.
- Global variables are unaffected by scopes and are always available.
- If the existence of a global variable in one file is declared using the extern keyword in another file,the data is available for use by the second file.
//C03:Global.cpp
//Demonstration of global variables
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int globe = 0;
void func();
void main(){globe = 12;cout << globe << endl;func();//Modify globecout << globe << endl;
}//C03:Global2.cpp
//Accessing external global variables
extern int globe;
//The linker resolves th reference
void func(){globe = 47;
}
output:

//C03:Global.cpp
//Demonstration of global variables
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int globe = 0;
void func();
void main(){int globe = 12;cout << globe << endl;func();//Modify globecout << globe << endl;
}//C03:Global2.cpp
//Accessing external global variables
extern int globe;
//The linker resolves th reference
void func(){globe = 47;
}
output:

原因解释
- 在
main()中定义的int globe = 12;屏蔽了全局的globe func()修改的是全局的globe,但main()中打印的是局部的- 因此即使func修改了全局变量,main中的输出仍为局部值
12
3.6.2局部变量(Local variables)
- Local variables are often called automatic variables because they automatically come into being when the scope is entered and automatically go away when the scope closes.
void func(){
int globe = 47;
}
3.6.3Static variables
- If you want a value to be persistent(持久的) throughout the life of a program,you can define a function’s local variable to be static and give it an initial value.
- The initialization is performed only the first time when the function is called,and the data retains(保留) its value between function calls.
- A static is unavailable outside the scope of the function
//C03:Static.cpp
//Using a static variable in a function
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void func(){static int i = 0;//int the functioncout << ++i << ",";
}
void main(){for (int x = 0;x<5;x++){func();}//cout i;//error
}
output:

//C03:FileStatic.cpp
//File scope demonstration.Compiling and
//lingking this file with FileStatic2.cpp
//will cause a linker error
//File scope means only available in this file;
static int fs = 0;
void main(){fs = 1;
}//C03:FileStatic2.cpp
//Trying to references fs
extern int fs;//linker error
void func(){fs = 100;//error
}
3.6.4Extern & linkage
Extern
- The extern keyword tells the compiler that a variable or a function exists,even if the compiler hasn’t yet seen it in the file currently being compiled.
- This variable or function may be defined in another file or further down in the current file.
linkage
- In an executing program,and identifier is represented by storagefont> in memory that holds a variable or a compiled function body.
internal linkage
- internal linkage means that storage is created to represent the identifier only for the file being compiled.
storage is created to represent the identifier意思是标识符所代表的数据在内存中的位置
- internal linkage在C++中通过keyword static 实现
external linkage
- external linkage means that a single piece of storage is created to represent the identifier for all files being compiled.(即非
static的全局变量,全局函数) - 在所有函数之外定义的变量,以及函数定义,默认具有external linkage。你可以同过
static关键字强制将其转为internal linkage,也可以通过extern关键字显示声明其为external linkage. - 局部变量只在函数调用期间暂时存在于stack上。linker(链接器)无法识别自动变量(即局部变量),因此它们没有连接属性(no linker)。
//C03:FileStatic.cpp
//internal linkage and external linkage
//linking this file with FileStatic2.cpp
static int fs = 0;//in the file
static void f(){};
int fe = 0;
extern void func(){};
void main(){fs = 1;func();
}//FileStatic.cpp
extern int fs;//linker error
extern int fe;
extern void f();//linker error
void func(){//fs = 100;//errorfe = 100;//f();//error
}
3.6.5常量(Constants)
-
#define PI 3.14159//这是一个replacement 并非Constants
//Its scope is: from #define to #undef
-
const double PI = 3.14159; //const -
const是一个实际变量,但值不可变 -
const必须有一个初始化的值
void f(const int a){};
int main(){f(5); // 调用 f 函数,传入字面值 5
}
这是可行的
3.6.6 volatile
- Whereas(尽管) the qualifier(修饰符)
consttells the compiler “This never changes”(Which allows the compiler to perform extra optimizations). - 修饰符
volatile则告诉编译器“你永远不知道这个值什么时候会改变” ,并且禁止编译器基于该变量的稳定性进行任何优化
3.7操作符与用法(Operators and their use)
3.7.1赋值(Assignment)
A = 4;
- A:an lvalue(左值),a distinct,named variable
- 4:an rvalue(右值),a constant,variable,or expression that can produce a value
3.7.2 数学的操作符(Mathematical operators)
- addition(+)
- subtraction(-)
- division(/)
- multiplication(*)
- modulus(%):this produces the remainder(余数) from integer division.
3.7.3 关系运算符(Relational operators)
- <,>,<=,>=,==,!=
- 这些运算符产生bool值,就像C语言一样
- 1 for true,0 for false.
3.7.4 逻辑操作符(Logical operators)
- &&,||,|,!
- The result is true if it has a non-zero value,and false if it has a value of zero.
3.7.5按位操作符(Bitwise operators)
- bitwise and (&)
- bitwise or (|)
- bitwise not /complement (~)//补码
- bitwise exclusive or / xor (^)//异或
- &=;|=;^=
3.7.6移位操作符(Shift operators)
- left-shift (<<)
- right-shift (>>)
- <<= ; >>=
3.7.7一元操作符(Unary operators)
- Bitwise not (~)
- logical not (!)
- unary minus (-) ; unary plus (+)
- increment (++); decrement (–)
- address-of (&)
- dereference (& and ->)//间接引用
- cast
- new;delelte
3.7.8三元操作符(The ternary operator)
-
c=a>b ? a : b
if (a> b ) c = a;else c = b;
3.7.9 逗号运算符(The comma operators)
//C03:CommaOperator.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void main(){int a =0,b=1,c=2,d=3,e=4;a = (b,c,d,e);cout << "a=" << a << endl;//The parentheses(圆括号) are critical here.Without//them,the statement will evaluete to.(a = b),c,d,e;cout << "a=" << a << endl;
}
output:

原因解释:
a = (b,c,d,e);
- 逗号表达式
(x, y)会先执行 x,再执行 y,并返回 y 的值。 - 所以
a = (b, c, d, e);实际含义是:a = e。 - 也就是逗号表达式(b,c,d,e) 会,顺序执行
b,c,d,e这些表达式,最终只返回最后一个表达式e的值 - 所以
a只赋值了一次:a = e;
(a = b),c,d,e;
- 它不是赋值语句(它不是
a = (……)) - 而是一个逗号表达式序列,主作用是执行它里面的每个子表达式,并返回最后一个表达式的值。
- 其中
(a = b)起到赋值操作,将b的值赋给a - 然后剩下的
c,d,e都是无副作用的值表达式,被执行但不改变任何东西 - 所以最后a = 1
3.7.10 表达式里常出的错误(Common pitfalls when using operators)
= ==
&& &
|| |
//C03:Pitfall.cpp
void main(){int a = 1,b = 1;while (a = b)//error{……}
}
3.7.11类型转换操作符(Casting operators)
-
Casting allows you to make this type conversation explicit
-
(type name) value
-
type name (argument)
int a = 100;
float b = float(a)
float c = (float) a
int d = int (5.5);
3.7.12 C++ explicit casts
-
static_cast<Type> (e): 用于在相关类型之间进行转换。
static_cast<int\>(5.5); -
reinter_cast<Type>(e): 处理不相关类型之间的转换,比如指针类型之间的“强制解释”。
int *p = reinterpret_cast<int*\>(0x12345678);🚨 非常危险,常用于底层编程。
-
const_cast<Type>(e): 去掉变量的
const限定。用于把const对象转换为非常量对象(⚠谨慎使用)const int*p = ……;int *q = const_cast<int*\>(p); -
dynamic_cast<Type>(e): 在运行时进行类型检查的转换。通常用于多态类之间的类型安全向下转换。
Base* bp = new Derived();
Derived* dp = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(bp); // 如果 bp 不是 Derived*,则返回 nullptr
3.7.13 sizeof操作符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void main(){cout << "bool:" << sizeof(bool) << endl;cout << "char:" << sizeof(char) << endl;cout << "int:" << sizeof(int) << endl;cout << "float:" << sizeof(float) << endl;cout << "double:" << sizeof(double) << endl;cout << "long double:" << sizeof(long double) << endl;
}
output:

结果可能会因为不一样的编译系统而不一样
3.7.14 asm关键字
- 你可以在C++程序中编写针对硬件的汇编代码
- 编写汇编语言时需要使用的具体语法依赖于(编译器)。
3.7.15显示操作符(Explicit operators)
-
These are keywords for bitwise and logical operators.(Not all complier(编译器) can support them )
-
and : && (logical and)
or : || (logical or)
not : ! (logical NOT)
not_eq: != (logical not-equivalne)
bitand: & (bitwise and)
and_eq: &= (bitwise and-assignment)
bitor: | (bitwise or)
or_eq: |= (bitwise or-assignment)
xor: ^ (bitwise exclusive-or)
xpr_eq: ^= (bitwise exclusive-or-assignment)
compl:~ (ones complement)
3.8复合类型创建(Composite type creation)
简述
- C++ 提供工具,允许你组合(compose)基础数据类型,从而创建更复杂的数据类型。
- 其中最重要的是结构体(struct),它是C++中**类(class)**的基础
3.8.1使用typedef创建别名(Aliasing names with typedef)
-
typedef existing-type alias-name
typedef int* IntPtr;IntPtr x,y;
3.8.2使用struct组合变量(Combining variables with struct)
- A struct is a way to collect a group of variables into a structure.
- The struct is the foundation for the class in the C++.
//C03:SimpleStruct.cpp
struct Structure1{char c;double b;
};
int main(){Structure1 s1,s2;Structure1* p = &s2;s1.c = 'a';//Select an element using a '.'s1.d = 0.00093;p->c = 'b';//Select an element using a '->'p->d = 10.5;return 0;
}
3.8.3使用enum澄清程序(Clarifying programs with enum)
-
An enumeration is a type that can hold a set of values specified by the user.
enum name{ASM,AUTO,BREAK} -
By default(默认) ,the values of enumerators(枚举值) are initialized increasing from 0
ASM = 0,AUTO = 1,BREAK = 2 -
An enumerator(枚举值) can be initialized by a constant-expression of integral type(整型常量表达式)
ASM = 1,AUTO = 5;这里这样写完后,BREAK就会默认为AUTO+1,所以BREAK = 6 -
It is used less in C++.(在C++中使用较少)
3.8.4使用union节省内存(Saving memory with union)
- Sometimes a program will handle different types of data using the same variable.
- A struct contains all the possible different types you might need to store.但是使用
struct时,每个成员都有独立的内存空间。 - An union is a special type of a class,where every member has the same address(每个成员共用同一个地址)
union A{int a;double b;
};
A x;

3.8.5 数组(Arrays)
概述
-
T[size]表示“由size个T类型元素组成的数组”。 -
The elements are indexed from 0 to size-1(元素索引范围)
-
There is no array assignment. (数组不能直接赋值)
意思就是说在C++中,不能把一个数组整体赋值给另一个数组
int a[3] = {1,2,3}; int b[3]; b = a;//错误!不能直接赋值数组原因:这是因为在C++中,数组名其实代表的时数组的首地址(在下文会提到),不是一个可以整体赋值的“对象”。并非是平常所理解的变量
-
The name of an array is the starting address of the array.
-
Initialization:
int v1[4] = {1,2,3,4}; char v2[] = {'a','b','c','\0'}; char v3[2] = {'a','b','\0'};//error 不可以超出数组size char v4[3] = {'a','b','c','\0'};//ok int v5[8] = {1,2,3,4};//部分初始化,未初始化的会系统默认初始化为0注意事项:
char v[3] = {'a','b','c'};是字符数组,这样编写不会报错,但它由于缺少’\0’,所以并不是一个字符串,如果执行cout << v;,程序将会崩溃,因为cout认为它是一个字符串,但它没有\0来标记结束。
Pointer and arrays
-
The name of an array can be used as a pointer to its initial elements.
-
Access a array can be achieved either through a pointer to an array plus an index or through a pointer to an element.
-
注意:大多数C++实现不会对数组访问进行范围检查(即你越界访问不会报错,但会导致未定义行为)。
int v[] = {1,2,3,4}; int* p1 = v;//pointer to initial element int* p2 = &v[2];v[2],*(v+2),*(p1+2),*p2都是3
3.9 调式提示(Debugging hints)
3.9.1预处理器调试标志(Pre-processor debugging flags)
这是用#define来控制是否输出调试信息的方式,编译时决定
示例:
#include <iostream>#define DEBUG // 注释掉这一行可以关闭调试输出int main() {int a = 5, b = 10;#ifdef DEBUGstd::cout << "Debug: a = " << a << ", b = " << b << std::endl;#endifstd::cout << "Sum = " << (a + b) << std::endl;return 0;
}DEBUG只是一个宏的名字,可以用DEBUG1等等代替
用法说明:
#ifdef DEBUG:只有在DEBUG被定义时,才会编译输出的调试代码。- 可以用来临时打开/关闭调试信息,不影响主逻辑
3.9.2运行时调试标志(Runtime debugging flags)
这是一种运行时控制调试信息的方式,通常用变量或命令行参数来控制。
示例:
#include <iostream>int main() {bool debugMode = true; // 运行时控制开关int a = 3, b = 7;if (debugMode) {std::cout << "[DEBUG] a = " << a << ", b = " << b << std::endl;}std::cout << "Product = " << (a * b) << std::endl;return 0;
}用法说明:
- 可以通过配置文件、命令行参数等方式改变
debugMode。 - 比预处理器方式灵活,不需要重新编译
3.9.3C语言的assert()宏
这是一个运行时断言,如果**表达式为假(false)**,程序会打印错误信息并终止
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert> // 引入 assertint divide(int a, int b) {assert(b != 0); // 如果 b 为 0,会终止程序return a / b;
}int main() {int result = divide(10, 2); // 正常std::cout << "Result = " << result << std::endl;result = divide(10, 0); // 触发断言失败return 0;
}用法说明:
assert()在Debug模式(开放时用的编译配置)下启用,在Release 模式(发布程序时用的优化配置)下会被编译器忽略(你可以用-DNDEBUG来关闭它)。- 非常适合用于验证前提条件,尤其是在开发测试时。
3.10函数地址(Function address)
概述
- Once(一旦) a function is compiled and loaded into the computer to be executed,it occupies a chunk(区块) of memory,and has an address.
- You can use function address with pointers just as you can use variable address.
3.10.1定义函数指针(Defining a function pointer)
void (*funcPtr)();表示:funcPtr是一个指向无参数、无返回值函数的指针funcPtr是一个指向函数的指针,该函数没有参数,也没有返回值。
void* funcPtr();表示:funcPtr是一个函数,它的返回类型时void*(即返回一个void指针)funcPtr是一个返回void*类型的函数(而不是指针)
3.10.2复杂的声明与定义(Complicated declarations & definitions)
- You will rarely(很少) need very complicated declarations and definitions.
- 逐步分析每一部分,并使用从右往左的规则来理解它。
float(*(*fp2)(int,int,float))(int)fp2是一个指向函数的指针,这个函数接受三个参数(int,int和float),并返回一个指向另一个函数的指针。- 那个被返回的函数接受一个
int参数,返回一个float值。
3.10.3使用函数指针(Using a function pointer)
- Once you define a pointer to a function,you must assign it to a function address before you can use it.
- The function name func denotes(表示) the address of a function
func().
//C03.PointerToFunction.cpp
//Defining and using a poinnter to a function
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void func(){cout << "func() called" << endl;
}int main(){void (*fp)();//Delare a function pointerfp = func; //Point to a function(*)fp(); //Call the function,func();void (*fp2)() = func; //Define and initialize(*fp2)(); //Call the functionreturn 0;
}
3.11动态存储分配(Dynamic storage allocation)
-
**new/new[]😗*creates dynamic objects.
new type(initialize);// individual objectnew type[size];//array
-
new/new[]returns a pointer that pointer to type. -
new[]dose not initialize the memory returned.使用
new[]创建数组时,不会自动初始化数组里的元素。 -
**delete/delete[]😗*destroy dynamic object.
delete pointername;// individualdelete[] pointername;// array
-
An object created by new must be destroyed by delete.
-
A pointer can be destroyed by delete/delete[] only once.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){int *p;p = new int(5); //individual obejctcout << *p << endl;delete p; //destory individual objectp = new int[5]; //arrayfor (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++)*(p+i)=i;for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++)cout << *(p+i) << "\t";delete[] p; //destroy arrayreturn 0;
}
output:

3.12 Summary
- Pointers
- References
- Operators : Casting operators
- Scope
- Const
- Static,extern
- New,delete
相关文章:

三、The C in C++
第三章主要讲解了 C 中继承自 C 语言的核心元素,包括函数创建、执行控制、操作符、数据类型、作用域、存储指示、复合类型创建等。 3.1 创建函数(Creating Functions) C允许函数重载,同名的函数可以根据参数类型和数量区分&…...

探索图像分类模型的 Flask 应用搭建之旅
最近深入研究了利用深度学习模型进行图像分类,并将其部署到 Flask 应用中的项目,过程中遇到了不少挑战,也收获了满满的知识,迫不及待想和大家分享一下。 一、项目背景与目标 在当今数字化的时代,图像数据呈爆炸式增长…...

OpenAI发布GPT-4.1系列模型——开发者可免费使用
OpenAI刚刚推出GPT-4.1模型家族,包含GPT-4.1、GPT-4.1 Mini和GPT-4.1 Nano三款模型。重点是——现在全部免费开放! 虽然技术升级值得关注,但真正具有变革意义的是开发者能通过Cursor、Windsurf和GitHub Copilot等平台立即免费调用这些模型。…...

自动化测试工具playwright中文文档-------14.Chrome 插件
介绍 注意 插件仅在以持久化上下文启动的 Chrome/Chromium 浏览器中工作。请谨慎使用自定义浏览器参数,因为其中一些可能会破坏 Playwright 的功能。 以下是获取位于 ./my-extension 的 Manifest v2 插件背景页面句柄的代码示例。 from playwright.sync_api imp…...

VGA显示
屏幕扫描形式 在回扫的过程中,电子枪不能发射电子,否则会影响荧光屏上既有图像的颜色,所以 回扫期间,需要进行行消隐,简单来说就是关闭电子枪。每行结束时,用行同步信号进行行 同步,图中从右上方向左下方的斜向虚线就是其回行扫示意图。 当整个屏幕的所有行都扫…...

微服务1--服务架构
系统架构 单体应用架构 特点:所有功能集中在一个应用中(如传统的 Spring Boot WAR 包)。 适用场景:小型项目、快速验证阶段。 优缺点: ✅ 开发简单,部署方便。 ❌ 扩展性差,技术栈耦合。 …...

鸿蒙应用元服务开发-Account Kit配置登录权限
一、场景介绍 华为账号登录是基于OAuth 2.0协议标准和OpenID Connect协议标准构建的OAuth2.0 授权登录系统,元服务可以方便地获取华为账号用户的身份标识,快速建立元服务内的用户体系。 用户打开元服务时,不需要用户点击登录/注册按钮&#…...

zg-docker详解与部署微服务实战与k8s
一. Docker课程 Docker简介 Docker是一个开源的容器引擎,有助于快速开发,docker更快地打包、测试以及部署应用程序,并可以缩短从编写到部署运行代码的周期。 使用宿主机的网络:即使用宿主机的网段。 联合文件系统-一个镜像,启动了多个容器,对于镜像中的文件a,多个容器…...

【含文档+PPT+源码】基于Python的快递服务管理系统【
毕业作品基于Django和HTML的快递网站设计与实现 课程目标: 教你从零开始部署运行项目,学习环境搭建、项目导入及部署,含项目源码、文档、数据库、软件等资料 课程简介: 本课程演示的是一款基于Python的快递服务管理系统&#x…...

嵌入式WebRTC轻量化SDK压缩至500K-800K ,为嵌入式设备节省Flash资源
一、SDK轻量化的核心技术实现 1、WebRTC库裁剪与模块化设计 EasyRTC针对嵌入式设备的资源限制,对原生WebRTC库进行深度裁剪,仅保留核心通信功能(如信令管理、编解码、网络传输等),移除冗余组件(如部分调试…...

JAVA学习-Stream
Stream Stream也叫Stream流,是Jdk8开始新增的一套API (java.util.stream.*),可以用于操作集合或者数 组的数据。 优势: Stream流大量的结合了Lambda的语法风格来编程,提供了一种更加强大,更加简单的方式 操作集合或者数…...

如何在同一个电脑配置多个jdk版本并随意切换
1.右键此电脑属性 2.点击高级系统配置 3.点击环境变量 4.进去后点击新建 变量名:JAVA_HOME_版本,来进行命名 变量值:jdk的路径即可,比如我的是D:\JAVA\JAVA11 5.创建完你所有的jdk版本之后接着新建 变量名:JAVA_HOME…...

网工_传输层协议概述
2025.02.19:网工老姜&小猿网学习笔记 第22节 传输层协议概述 2.1 进程之间的通信2.2 传输层的两个主要协议2.3 传输层的端口2.3.1 端口号 2.4 本章小结 2.1 进程之间的通信 前三层解决了数据从主机到主机的问题,也就是,我们现在已经可以把…...

《java面试宝典》之java多线程面试题
1:什么是线程? 轻量级的进程 2:线程的三个部分是? 处理机 代码 数据 3:为什么使用多线程 使UI响应更快 利用多处理器系统 简化建模 4:代码示例:Java中实现多线程的两种方式,包括如何…...

5款电脑健康状况监测软件
鲁大师:专业且免费,能检测电脑硬件配置,辨别硬件真伪,检查电脑病毒隐患。可一键清理系统垃圾,提升电脑性能。还能全程监护硬件状态,实时检测硬件温度变化,让用户轻松掌握电脑健康状况。360 安全…...

JWT令牌:实现安全会话跟踪与登录认证的利器
摘要:本文深入探讨了JWT令牌在实现会话跟踪和登录认证方面的应用,详细介绍了JWT令牌的概念、组成、生成与校验方法,以及在实际案例中如何通过JWT令牌进行会话跟踪和登录认证的具体实现步骤,为系统的安全认证机制提供了全面且深入的…...

uni-app/微信小程序接入腾讯位置服务地图选点插件
uni-app/微信小程序接入腾讯位置服务地图选点插件 0、常出现的错误及解决方法0.1插件未授权使用(见步骤1)0.2小程序类目不符合引用该类目插件的要求或主体类型不符合要求(见步骤1)0.3需要在app.json中声明permission scope.userLo…...

3款顶流云电脑与传统电脑性能PK战:START云游戏/无影云/ToDesk云电脑谁更流畅?
这里写目录标题 一、前言二、本地机器配置环境三、START云游戏/无影云/ToDesk云电脑配置对比3.1 START云游戏3.2 无影云个人版3.3 ToDesk云电脑 四、本地电脑与云电脑性能实战4.1 游戏场景体验4.1.1 本地电脑测试4.1.2 云电脑测试英雄联盟黑神话悟空其他游戏 4.2 主流设计场景体…...

WINUI——Background小结
在 WinUI/UWP XAML 中,Background(或其他颜色属性)支持 多种颜色表示方式,包括以下三种主流格式: 1. RGB 十六进制(不透明) 格式:#RRGGBB特点…...
和闭源(仅限内部),以及公共(全员可访问)和内部(特定团队/项目组)四个维度)
公司内部自建知识共享的方式分类、详细步骤及表格总结,分为开源(对外公开)和闭源(仅限内部),以及公共(全员可访问)和内部(特定团队/项目组)四个维度
以下是公司内部自建知识共享的方式分类、详细步骤及表格总结,分为开源(对外公开)和闭源(仅限内部),以及公共(全员可访问)和内部(特定团队/项目组)四个维度&am…...

cursor AI编辑器的详细使用
以下是Cursor AI编辑器的详细使用介绍,涵盖核心功能、安装配置、使用技巧、高级应用及常见问题解决方案,结合了多个权威来源的实践指南和最新技术动态: 一、Cursor AI简介与核心功能 定位与架构 Cursor是基于Visual Studio Code(V…...

js逆向入门实战某某观察网响应数据解密
(base64解码 base64解码)地址:aHR0cHM6Ly93d3cuc3dndWFuY2hhLmNvbS9ob21lL2NpdHktZGV0YWlsP2NvZGU9MzEwMTAw 分析过程 1.抓数据包,发现响应数据是加密字符串。 2.对于这种回显数据解密,大概率通过拦截器实现,搜索intercepto…...

Ubuntu安装yum遇到Package ‘yum‘ has no installation candidate
环境说明 Window11,WSL2,Ubuntu24.04 错误描述 rootLAPTOP:~# apt-get install yum Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done Package yum is not available, but is referred to by anot…...

爱普生SG3225EEN低抖动差分晶振在网络通信的应用
在当今数字化时代,网络通信的飞速发展对数据传输的准确性、稳定性和高效性提出了极为严苛的要求。从 5G 通信网络的大规模部署,到数据中心的海量数据交换,再到智能家居系统的互联互通,每一个环节都离不开精准稳定的时钟信号作为支…...

软考教材重点内容 信息安全工程师 第22章 网站安全需求分析与安全保护工程
22.1.1 网站安全概念 网站是一个基于 B/S 技术架构的综合信息服务平台,主要提供网页信息及业务后台对外接口服务。一般网站涉及网络通信、操作系统、数据库、Web 服务器软件、Web 应用、浏览器、域名服务以及 HTML, XML,SSL; Web Services 等相关协议,同…...

数智读书笔记系列029 《代数大脑:揭秘智能背后的逻辑》
《代数大脑:揭秘智能背后的逻辑》书籍简介 作者简介 加里F. 马库斯(Gary F. Marcus)是纽约大学心理学荣休教授、人工智能企业家,曾创立Geometric Intelligence(后被Uber收购)和Robust.AI公司。他在神经科学、语言学和人工智能领域发表了大量论文,并著有《重启AI》等多部…...

UWB技术与5G、物联网结合的应用前景
一、核心应用场景与优势 工业自动化与智能制造 高精度设备协同:UWB技术(3cm定位精度)与5G(1ms级时延)结合,可实时追踪AGV、机械臂等设备位置,优化生产节拍,提升效率20…...
)
vue + element-plus自定义表单验证(修改密码业务)
写一个vue组件Password.vue 没有表单验证只有3个表单项 <template><div><el-form><el-form-item label"旧密码"><el-input></el-input></el-form-item><el-form-item label"新密码"><el-input>&l…...

如何将 Vue-FastAPI-Admin 项目的数据库从 SQLite 切换到 MySQL?
近期在github上看到一个开源项目,vue-fastapi-admin。它基于 FastAPI Vue3 Naive UI 的现代化前后端分离开发平台,融合了 RBAC 权限管理、动态路由和 JWT 鉴权,助力中小型应用快速搭建,也可用于学习参考。 由于该项目中数据库用…...

K8S运维实战之集群证书升级与容器运行时更换全记录
第一部分:Kubernetes集群证书升级实战 tips:此博文只演示一个节点作为示范,所有的集群节点步骤都可以参考。 项目背景 某金融业务系统Kubernetes集群即将面临生产证书集中过期风险(核心组件证书剩余有效期不足90天),…...

idea如何克隆拉取远程git项目到本地
概述 idea如何克隆拉取远程git项目到本地?方法很简单,找到入口,跟着引导窗口下一步下一步即可。 方法 File -> New -> Project from Version Control...然后根据引导窗口,一步一步操作即可...

聚铭网络亮相2025超云产品技术大会,联合发布“铭智安全运营大模型一体机及解决方案”
4月11日,于南京银城皇冠假日酒店举办的2025超云产品技术大会圆满落幕。聚铭网络受邀出席本次大会,并与超云联合发布了“铭智安全运营大模型一体机及解决方案”,为智能安全运营领域带来了全新突破。 会议背景 在全球人工智能技术加速产业化…...
)
成员访问运算符重载(详解)
目录 成员访问运算符 两层结构下的使用 三层结构下的使用(难点) 内存分析 成员访问运算符 成员访问运算符包括箭头访问运算符 -> 和解引用运算符 * ,它们是指针操作最常用的两个运算符。我们先来看箭头运算符 -> 箭头运算符只能以…...

无感改造,完美监控:Docker 多阶段构建 Go 应用无侵入观测
作者:牧思 背景 随着云原生的普及,Golang 编程语言变得越来越热门。相比 Java,Golang 凭借其轻量,易学习的特点得到了越来越多工程师的青睐,然而由于 Golang 应用需要被编译成二进制文件再进行运行,Golan…...

项目后期发现重大漏洞,如何紧急修复
项目后期发现重大漏洞的紧急修复关键在于: 迅速识别漏洞根本原因、制定修复优先级、协调团队资源、实施快速修复和验证、总结经验防止重复发生。 其中,迅速识别漏洞根本原因是最为关键的一步。找到漏洞的根本原因有助于确保修复措施不仅解决眼前的问题&a…...

设计模式:状态模式 - 复杂状态切换的优雅之道
一、为什么用状态模式? 在开发过程中,你是否遇到过这样的难题:对象需要根据不同的状态执行不同行为,但代码中却充斥着大量的if-else或switch-case语句? 随着状态的增多,代码变得臃肿且难以阅读࿰…...

【AI提示词】业务开发经理
提示说明 业务开发经理旨在帮助用户构建一个高效、有洞察力的业务发展角色,能够在竞争激烈的市场中寻找并抓住商机。 提示词 # 角色 业务开发经理专家## 注意 - 业务开发经理应具备强烈的市场洞察力和人际沟通能力。 - 专家设计应考虑业务发展的实际需求和挑战。…...

发电机参数详解
一、发电机参数体系概述 发电机作为将机械能转换为电能的核心设备,其参数体系涵盖电气、机械、结构、性能、控制五大维度,是设备选型、运行维护、故障诊断的重要依据。参数体系的完整性和准确性直接影响电力系统的稳定性与经济性。以下通过思维导图展示发电机参数的整体架构…...

每天五分钟深度学习PyTorch:RNN CELL模型原理以及搭建
本文重点 RNN Cell(循环神经网络单元)是循环神经网络(RNN)的核心组成部分,用于处理序列数据中的每个时间步,并维护隐藏状态以捕获序列中的时间依赖关系。 RNN CELL的结构 RNN是一个循环结构,它可以看作是RNN CELL的循环,RNN CELL的结构如下图所示,RNN CELL不断进行…...
 的波形发生器)
设计和实现一个基于 DDS(直接数字频率合成) 的波形发生器
设计和实现一个基于 DDS(直接数字频率合成) 的波形发生器 1. 学习和理解IP软核和DDS 关于 IP 核的使用方法 IP 核:在 FPGA 设计中,IP 核(Intellectual Property Core)是由硬件描述语言(HDL&a…...

RCEP框架下eBay日本站选品战略重构:五维解析关税红利机遇
2024年RCEP深化实施背景下,亚太跨境电商生态迎来结构性变革。作为协定核心成员的日本市场,其跨境电商平台正经历新一轮价值重构。本文将聚焦eBay日本站,从政策解读到实操路径,系统拆解跨境卖家的战略机遇。 一、关税递减机制下的…...

使用 Node.js、Express 和 React 构建强大的 API
了解如何使用 Node.js、Express 和 React 创建一个强大且动态的 API。这个综合指南将引导你从设置开发环境开始,到集成 React 前端,并利用 APIPost 进行高效的 API 测试。无论你是初学者还是经验丰富的开发者,这篇文章都适合你。 今天&#…...

如何争取高层对项目的支持
争取高层对项目的支持关键在于明确项目的战略价值、展示其可行性与回报、以及有效的沟通和利益对接。高层管理者通常关注的是项目如何帮助公司实现整体战略目标,如何提高企业的竞争力或收益。在争取支持的过程中,项目经理需要清楚地表达项目的潜在价值&a…...

git合并分支原理
Git合并的原理是基于三方合并(three-way merge)算法,它通过比较三个快照来合并不同分支上的更改。这三个快照包括两个要合并的分支的最新提交和它们的共同祖先提交。合并过程并不是简单地按照提交时间来进行,而是通过比较这些快照…...

最短路问题
最短路问题 最短路问题 最短路算法(Shortest Path Algorithm)是用来解决图中两点之间的最短路径的问题。常见的应用包括:地图导航、网络路由、游戏寻路等。根据图的性质(有向/无向、是否有负权边)和需求(…...

ARM Cortex汇编伪指令
在ARM架构(尤其是Cortex-M系列MCU)的汇编中,伪指令(Pseudo-Instructions)是由汇编器解释的特殊指令,用于定义数据、符号、代码结构或控制汇编过程。以下是常用的ARM汇编伪指令分类及说明: 一、…...

如何在vue3项目中使用 AbortController取消axios请求
在 Vue3 项目中通过 AbortController 取消 Axios 请求,可以通过以下 结构化步骤 实现。我们结合组合式 API(Composition API)和现代前端实践演示: 一、基础实现(单个请求) 1. 创建组件逻辑 <script s…...

Bright+Data网页解锁器在旅游行业的创新实践
引言 随着在线旅游平台的快速发展,网络爬虫技术成为获取旅游数据的重要手段。然而,主流旅游网站(如去哪儿网、携程等)普遍部署了反爬虫机制,包括IP封禁、验证码验证、请求频率限制等技术手段,严重影响了传…...

SpringMVC 执行流程
前言: 在前后端分离的情况下,SpringMVC 的执行流程主要集中在处理 RESTful 请求和返回 JSON 数据。这里的 Controller 会直接返回数据,而不是视图。我们通常会使用 RestController 和 RequestMapping 来处理请求,ResponseBody 会…...

STM32G0单片机自带RTC
STM32有个自带RTC外设,外接32.768KHz的晶振后可得到相对精确的计时功能。 实测了一个一小时快个1秒多。 1 cubeMX设置了RTC后自动生成的初始化代码如下 static void MX_RTC_Init(void) {/* USER CODE BEGIN RTC_Init 0 *//* USER CODE END RTC_Init 0 */RTC_TimeT…...
