Linux电源管理(五),发热管理(thermal),温度控制
更多linux系统电源管理相关的内容请看:Linux电源管理、功耗管理 和 发热管理 (CPUFreq、CPUIdle、RPM、thermal、睡眠 和 唤醒)-CSDN博客
本文主要基于linux-5.4.18版本的内核代码进行分析。
1 简介
1.1 硬件知识
CPU等芯片在工作时会产生大量热量,导致硬件温度升高,而每个芯片都有自己的工作温度区间(例如FT-2000四核处理器的工作温度如下图所示)。当芯片的温度不在这个区间内时,芯片将无法正常工作。

![]() 《FT-2000/4 系列处理器数据手册》1 简介
《FT-2000/4 系列处理器数据手册》1 简介
为了控制硬件温度,硬件上有两类降温设备(Cooling device):
- 主动降温(Active Cooling)设备,一般是风扇;
- 被动降温(Passive Cooling)设备,一般是发热的芯片本身,通过降低频率或者电压来减少热量的产生。
1.2 温度控制的方案

《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》3.10 Thermal Management Concepts
如上图所示,很多硬件设计中,CPU的温度传感器和风扇是直接受EC (Embedded Controller)控制的,所以出现了两种温度控制的方案:
- 第一种、完全由EC来控制硬件温度,linux系统不干预;
- 第二种、Linux系统通过EC来控制硬件温度
本文主要分析第二种方案。
2 thermal_zone_device
2.1 简介
可以获取温度的设备抽象为thermal_zone_device, 如Temperature Sensor等。
《SoC底层软件低功耗系统设计与实现》 9.1.2 模块功能详解
2.2 数据结构
2.2.1 struct thermal_zone_device
//include/linux/thermal.h
struct thermal_zone_device {int temperature; //current temperature. int last_temperature; //previous temperature readint prev_low_trip; //上⼀次温控的低温触发点int prev_high_trip; //上⼀次温控的⾼温触发点struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops;struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;struct thermal_governor *governor;struct delayed_work poll_queue;......
};register和unregister
struct thermal_zone_device *thermal_zone_device_register(const char *, int, int,void *, struct thermal_zone_device_ops *,struct thermal_zone_params *, int, int);void thermal_zone_device_unregister(struct thermal_zone_device *);2.2.2 struct thermal_zone_device_ops
//include/linux/thermal.h
struct thermal_zone_device_ops {int (*bind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,struct thermal_cooling_device *);int (*unbind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,struct thermal_cooling_device *);int (*get_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);int (*set_trips) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);int (*get_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,enum thermal_device_mode *);int (*set_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,enum thermal_device_mode);int (*get_trip_type) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,enum thermal_trip_type *);int (*get_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);int (*set_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);int (*get_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);int (*set_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);int (*get_crit_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);int (*set_emul_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int);int (*get_trend) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,enum thermal_trend *); int (*notify) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,enum thermal_trip_type);
};2.3 温度状态 和 温度阈值(trip point)
2.3.1 简介
软件上有四个温度阈值,分别是active、passive、hot和critical。
当实际温度超过active温度阈值时,应该执行主动降温操作;
当实际温度超过pssive温度阈值时,应该执行被动降温操作;
当实际温度超过hot温度阈值时,在支持ACPI的设备上应该执行S4(挂起到硬盘)操作;
当实际温度超过critical温度阈值时,应该执行关机操作。
当实际温度超过某个阈值后,具体执行什么操作请看下面的 “4 绑定zone_device的trip points和cooling_device” 小节
2.3.2 数据结构
//include/linux/thermal.h
/*** struct thermal_trip - representation of a point in temperature domain* @np: pointer to struct device_node that this trip point was created from* @temperature: temperature value in miliCelsius* @hysteresis: relative hysteresis in miliCelsius* @type: trip point type*/struct thermal_trip {struct device_node *np;int temperature;int hysteresis;enum thermal_trip_type type;
};//include/linux/thermal.h
enum thermal_trip_type {THERMAL_TRIP_ACTIVE = 0,THERMAL_TRIP_PASSIVE,THERMAL_TRIP_HOT,THERMAL_TRIP_CRITICAL,
};2.3.3 通过设备树指定trip points
trips {cpu_alert0: cpu-alert0 {temperature = <90000>; /* millicelsius */hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */type = "active";}; cpu_alert1: cpu-alert1 {temperature = <100000>; /* millicelsius */hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */type = "passive";}; cpu_crit: cpu-crit {temperature = <125000>; /* millicelsius */hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */type = "critical";}; };上面的设备树信息说明
The trip node is a node to describe a point in the temperature domain in which the system takes an action. This node describes just the point, not the action.
Required properties:
- temperature: An integer indicating the trip temperature level,
Type: signed in millicelsius.
Size: one cell
- hysteresis: A low hysteresis value on temperature property (above).
Type: unsigned This is a relative value, in millicelsius.
Size: one cell
- type: a string containing the trip type. Expected values are:
"active": A trip point to enable active cooling
"passive": A trip point to enable passive cooling
"hot": A trip point to notify emergency
"critical": Hardware not reliable.
Documentation/devicetree/bindings/thermal/thermal.txt
2.3.4 通过ACPI Source Language (ASL)来指定trip points
Thermal Objects
<1> _ACx (Active Cooling)
This optional object, if present under a thermal zone, returns the temperature trip point at which OSPM must start or
stop Active cooling, where x is a value between 0 and 9 that designates multiple active cooling levels of the thermal
zone.
<2> _PSV (Passive)
This optional object, if present under a thermal zone, evaluates to the temperature at which OSPM must activate
passive cooling policy.
<3> _CRT (Critical Temperature)
This object, when defined under a thermal zone, returns the critical temperature at which OSPM must shutdown the
system.
<4> _HOT (Hot Temperature)
This optional object, when defined under a thermal zone, returns the critical temperature at which OSPM may choose
to transition the system into the S4 sleeping state.
《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》11.4 Thermal Objects
示例
ThermalZone (TZ0) {Method(_PSV) { Return(_C2K(70)) } /* passive cooling temp */Method(_HOT) { Return(_C2K(85)) } /* hot temp */Method(_CRT) { Return(_C2K(95)) } /* critical temp */......
} /* ThermalZone(TZ0) */2.3.5 查看trip points信息
/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zoneX/trip_point_0_type
/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zoneX/trip_point_0_temp
/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zoneX/trip_point_0_hyst示例
# cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone4/trip_point_0_type
critical
# cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone4/trip_point_0_temp
110050
# cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone4/trip_point_0_hyst
02.4 查看或者设置 thermal_zone_device信息
/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zoneX/

3 cooling_device
3.1 简介
可以控制温度的设备抽象为thermal_cooling_device, 如⻛扇、CPU、DDR、GPU等。
《SoC底层软件低功耗系统设计与实现》 9.1.2 模块功能详解
主动(active)降温设备 和 被动(passive)降温设备
Cooling devices are nodes providing control on power dissipation. There are essentially two ways to provide control on power dissipation. First is by means of regulating device performance, which is known as passive cooling. A typical passive cooling is a CPU that has dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS), and uses lower frequencies as cooling states. Second is by means of activating devices in order to remove the dissipated heat, which is known as active cooling, e.g. regulating fan speeds. In both cases, cooling devices shall have a way to determine the state of cooling in which the device is.
Documentation/devicetree/bindings/thermal/thermal.txt
Active cooling devices typically consume power and produce some amount of noise when enabled. These devices
attempt to cool a thermal zone through the removal of heat rather than limiting the performance of a device to address
an adverse thermal condition.
《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》11.1.4 Active Cooling
Passive cooling controls are able to cool a thermal zone without creating noise and without consuming additional
power (actually saving power), but do so by decreasing the performance of the devices in the zone .
《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》11.1.5 Passive Cooling
3.2 数据结构
3.2.1 struct thermal_cooling_device;
//include/linux/thermal.h
struct thermal_cooling_device {int id; char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];struct device device;struct device_node *np;void *devdata;void *stats;const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops;bool updated; /* true if the cooling device does not need update */struct mutex lock; /* protect thermal_instances list */struct list_head thermal_instances;struct list_head node;
};3.2.2 struct thermal_cooling_device_ops;
//include/linux/thermal.h
struct thermal_cooling_device_ops {int (*get_max_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);int (*get_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);int (*set_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long);int (*get_requested_power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,struct thermal_zone_device *, u32 *);int (*state2power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,struct thermal_zone_device *, unsigned long, u32 *);int (*power2state)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,struct thermal_zone_device *, u32, unsigned long *);
};3.3 states
3.3.1 简介
冷却设备(cooling device)维护一个冷却(cooling)等级,即状态(state),一般状态越高,系统的冷却需求越高,所采取的冷却措施也可能更激进。冷却设备根据不同等级的冷却需求进行冷却行为。冷却设备只根据state进行冷却操作,是实施者,而state的计算由thermal governor完成。
《SoC底层软件低功耗系统设计与实现》 9.1.2 模块功能详解
Any cooling device has a range of cooling states (i.e. different levels of heat dissipation). For example a fan's cooling states correspond to the different fan speeds possible. Cooling states are referred to by single unsigned integers, where larger numbers mean greater heat dissipation. The precise set of cooling states associated with a device should be defined in a particular device's binding.
Documentation/devicetree/bindings/thermal/thermal.txt
3.3.2 设置cooling device的states
3.3.2.1 通过设备树指定PWM风扇的states (cooling-levels)
//arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos5410-odroidxu.dtsfan0: pwm-fan {compatible = "pwm-fan";pwms = <&pwm 0 20972 0>;#cooling-cells = <2>;cooling-levels = <0 130 170 230>;};cooling-levels : PWM duty cycle values in a range from 0 to 255 which correspond to thermal cooling states
Documentation/devicetree/bindings/hwmon/pwm-fan.txt
3.3.2.2 通过设备树指定CPU的states (operating-points)
//Documentation/devicetree/bindings/thermal/thermal.txt
cpus {/* * Here is an example of describing a cooling device for a DVFS* capable CPU. The CPU node describes its four OPPs.* The cooling states possible are 0..3, and they are* used as OPP indexes. The minimum cooling state is 0, which means* all four OPPs can be available to the system. The maximum* cooling state is 3, which means only the lowest OPPs (198MHz@0.85V)* can be available in the system.*/cpu0: cpu@0 {...operating-points = < /* kHz uV */ 970000 1200000 792000 1100000 396000 950000198000 850000>;#cooling-cells = <2>; /* min followed by max */};...
};3.3.3.3 通过ACPI Source Language (ASL)指定风扇的states (转速)
根据下面的 “7.2.2 控制风扇的转速(fan_set_cur_state)” 章节信息,使用ACPI 1.0规范时,风扇对应的cooling device只有2种states,即打开(D0) 和 关闭(D3);使用ACPI 4.0规范时,可以通过“_FPS (Fan Performance States)”来指定多个states。
3.3.3.4 通过ACPI Source Language (ASL)指定CPU的states
_TSS (Throttling Supported States)
This optional object indicates to OSPM the number of supported processor throttling states that a platform supports.



《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》
8.4.5.2 _TSS (Throttling Supported States)
ASL示例
Scope(\_SB) {Device(CPU0) {Name(_HID, "ACPI0007")Name(_UID, 0)......// Throttling Supported States// The values shown are for exemplary purposes onlyName(_TSS, Package() {// Read: freq percentage, power, latency, control, statusPackage() {0x64, 1000, 0x0, 0x7, 0x0}, // Throttle off (100%)Package() {0x58, 800, 0x0, 0xF, 0x0}, // 87.5%Package() {0x4B, 600, 0x0, 0xE, 0x0}, // 75%Package() {0x3F, 400, 0x0, 0xD, 0x0} // 62.5%})......}......
} 《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》
11.7.3 Example: Thermal Zone with Multiple Devices
对应的驱动初始化流程请看“7.3.2” 小节
3.3.3 查看cooling device的states信息
/sys/class/thermal/cooling_device0/cur_state
/sys/class/thermal/cooling_device0/max_state
3.4 查看cooling_device信息
/sys/class/thermal/cooling_deviceX

4 绑定zone_device的trip points和cooling_device
4.1 简介
thermal_zone_device_register()函数在注册thermal_zone_device时,会调用bind_tz()函数,bind_tz()会遍历已经注册的cooling device,然后执行cooling device和当前注册的thermal_zone_device绑定工作。
thermal_cooling_device_register()函数在注册thermal_cooling_device时,会调用bind_cdev()函数,bind_tz()会遍历已经注册的zone device,然后执行zone device和当前注册的thermal_cooling_device绑定工作。
bind_tz() 和 bind_cdev()最终都会执行struct thermal_zone_device_ops中的bind()函数 和 struct thermal_bind_params中的match()函数来完成具体工作,所以需要实现bind() 或者 match()函数才能完成绑定工作。
最终的绑定工作通过thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device()函数实现,绑定关系通过struct thermal_instance记录。
4.2 数据结构
/** This structure is used to describe the behavior of* a certain cooling device on a certain trip point* in a certain thermal zone*/
struct thermal_instance {int id;char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];struct thermal_zone_device *tz;struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev;int trip;bool initialized;unsigned long upper; /* Highest cooling state for this trip point */unsigned long lower; /* Lowest cooling state for this trip point */unsigned long target; /* expected cooling state */char attr_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];struct device_attribute attr;char weight_attr_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];struct device_attribute weight_attr;struct list_head tz_node; /* node in tz->thermal_instances */struct list_head cdev_node; /* node in cdev->thermal_instances */unsigned int weight; /* The weight of the cooling device */
};4.3 绑定函数
This interface function bind a thermal cooling device to the certain trip point of a thermal zone device.
This function is usually called in the thermal zone device .bind callback.
int thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip,struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev,unsigned long upper, unsigned long lower,unsigned int weight);4.4 指定thermal zone device的每个trip point和 cooling device之间的绑定关系
4.4.1 设备树
trips {cpu_alert0: cpu-alert0 { //trip pointtemperature = <90000>; /* millicelsius */hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */type = "active";};......cooling-maps {map0 {trip = <&cpu_alert0>;cooling-device = <&fan0 THERMAL_NO_LIMIT 4>; };......4.4.2 ACPI
_ACx (Active Cooling)
_ALx (Active List)
_PSV (Passive)
_PSL (Passive List)
《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》
11.4 Thermal Objects
4.5 查看绑定关系
# ls /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/cdev* -l
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 5月 11 18:51 /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/cdev0 -> ../cooling_device9
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 5月 11 18:51 /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/cdev0_trip_point
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 5月 11 18:51 /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/cdev0_weight
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 5月 11 18:51 /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/cdev1 -> ../cooling_device10
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 5月 11 18:51 /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/cdev1_trip_point
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 5月 11 18:51 /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/cdev1_weight
# cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/cdev0_trip_point
2
# cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/cdev1_trip_point
1
# cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/trip_point_2_temp
80000
# cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone7/trip_point_1_temp
60000
上面的信息显示thermal_zone7的1号trip point (60摄氏度)和cooling_device10绑定在一起。2号trip point (80摄氏度)和cooling_device9绑定在一起
5 governors
5.1 简介
温控策略抽象为thermal_governor, ⽐如step_wise、bang_bang等。
《SoC底层软件低功耗系统设计与实现》 9.1.2 模块功能详解
5.2 现有的governors
5.2.1 step_wise
/** If the temperature is higher than a trip point,* a. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISING, use higher cooling* state for this trip point* b. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROPPING, do nothing* c. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISE_FULL, use upper limit* for this trip point* d. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROP_FULL, use lower limit* for this trip point* If the temperature is lower than a trip point,* a. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISING, do nothing* b. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROPPING, use lower cooling* state for this trip point, if the cooling state already* equals lower limit, deactivate the thermal instance* c. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISE_FULL, do nothing* d. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROP_FULL, use lower limit,* if the cooling state already equals lower limit,* deactivate the thermal instance*/drivers/thermal/step_wise.c
5.2.2 power_allocator
5.2.3 bang_bang
* Regulation Logic: a two point regulation, deliver cooling state depending* on the previous state shown in this diagram:** Fan: OFF ON** |* |* trip_temp: +---->+* | | ^* | | |* | | Temperature* (trip_temp - hyst): +<----+* |* |* |** * If the fan is not running and temperature exceeds trip_temp, the fan* gets turned on.* * In case the fan is running, temperature must fall below* (trip_temp - hyst) so that the fan gets turned off again.*drivers/thermal/gov_bang_bang.c
5.2.4 user_space
Notifies user space about thermal events
drivers/thermal/user_space.c
5.2.5 fair_share
* Throttling Logic: This uses three parameters to calculate the new* throttle state of the cooling devices associated with the given zone.** Parameters used for Throttling:* P1. max_state: Maximum throttle state exposed by the cooling device.* P2. percentage[i]/100:* How 'effective' the 'i'th device is, in cooling the given zone.* P3. cur_trip_level/max_no_of_trips:* This describes the extent to which the devices should be throttled.* We do not want to throttle too much when we trip a lower temperature,* whereas the throttling is at full swing if we trip critical levels.* (Heavily assumes the trip points are in ascending order)* new_state of cooling device = P3 * P2 * P1drivers/thermal/fair_share.c
5.3 查看和设置governor
/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zoneX/available_policies
/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zoneX/policy
6 核心代码流程
6.1 简介
内核代码中会循环读取温度数据,如果温度超过某个trip point温度,就会启动和这个trip point绑定的cooling device开始降温工作。
6.2 代码流程
轮训工作通过工作项实现
thermal_zone_device_register();-> INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&tz->poll_queue, thermal_zone_device_check);工作项处理函数thermal_zone_device_check()的流程如下:
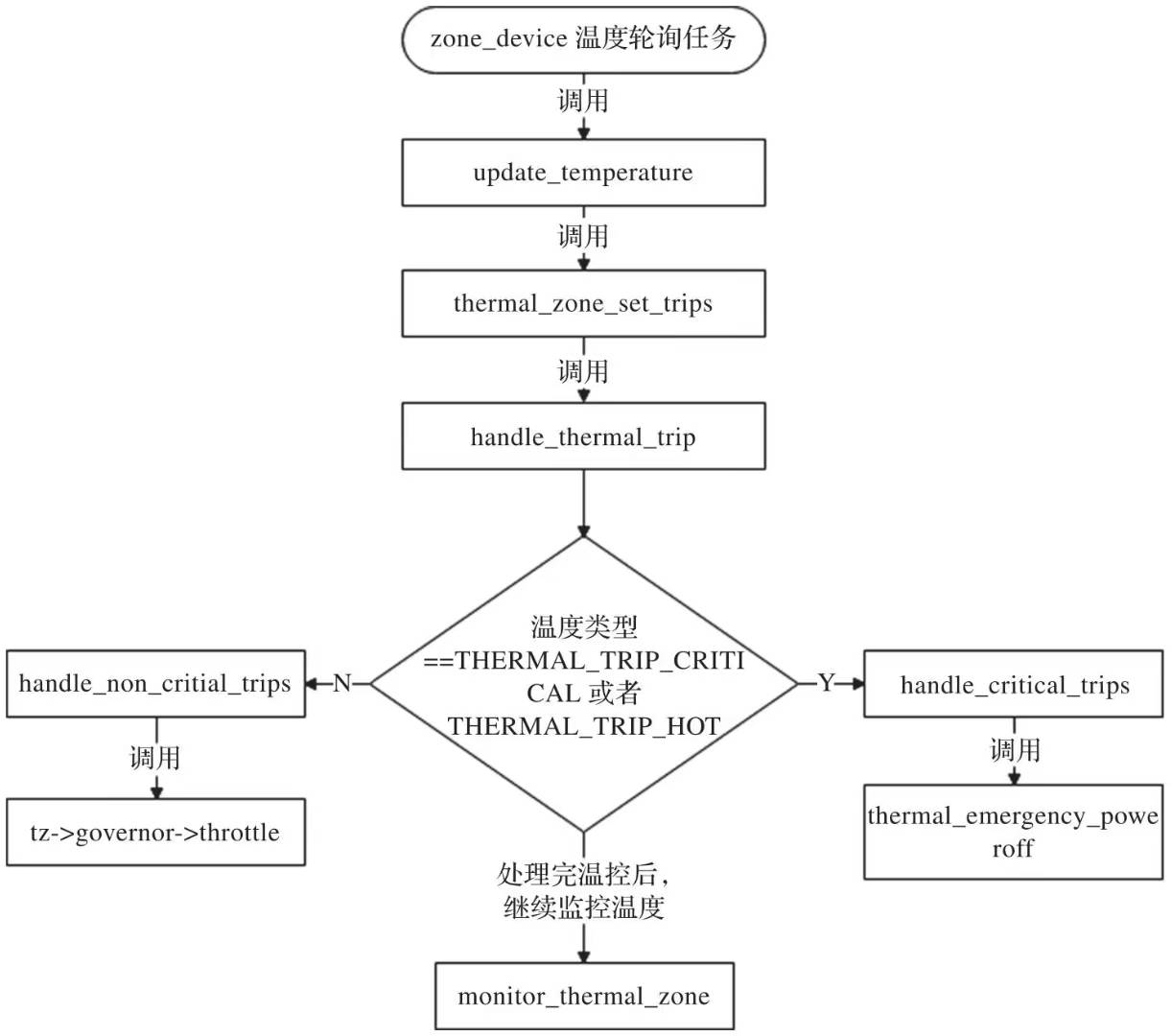
《SoC底层软件低功耗系统设计与实现》9.1.6 关于critical事件和非critical事件的处理流程
monitor_thermal_zone()函数会重新添加工作项,以此来达到循环执行的效果 (循环的间隔时间通过struct thermal_zone_device中的passive_delay变量和polling_delay变量控制)。
monitor_thermal_zone();-> thermal_zone_device_set_polling();-> mod_delayed_work(system_freezable_power_efficient_wq, &tz->poll_queue, <时间>);tz->governor->throttle()会执行governors的控温逻辑,选择cooling device的states,然后调用cdev->ops->set_cur_state();
以step_wise(governor)为例
step_wise_throttle();-> thermal_zone_trip_update(tz, trip);-> trend = get_tz_trend(tz, trip);-> instance->target = get_target_state(instance, trend, throttle);-> thermal_cdev_update();-> cdev->ops->set_cur_state();关键函数get_target_state()的注释如下:
//drivers/thermal/step_wise.c
/** If the temperature is higher than a trip point,* a. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISING, use higher cooling* state for this trip point* b. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROPPING, do nothing* c. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISE_FULL, use upper limit* for this trip point* d. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROP_FULL, use lower limit* for this trip point* If the temperature is lower than a trip point,* a. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISING, do nothing* b. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROPPING, use lower cooling* state for this trip point, if the cooling state already* equals lower limit, deactivate the thermal instance* c. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISE_FULL, do nothing* d. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROP_FULL, use lower limit,* if the cooling state already equals lower limit,* deactivate the thermal instance*/
static unsigned long get_target_state(struct thermal_instance *instance,enum thermal_trend trend, bool throttle)
{......
}7 基于ACPI的温控驱动分析
7.1 thermal_zone_device
7.1.1 数据结构
7.1.1.1 struct acpi_driver acpi_thermal_driver;
//include/acpi/acpi_drivers.h
#define ACPI_THERMAL_HID "LNXTHERM"//drivers/acpi/thermal.c
static const struct acpi_device_id thermal_device_ids[] = {{ACPI_THERMAL_HID, 0},{"", 0},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(acpi, thermal_device_ids);static struct acpi_driver acpi_thermal_driver = {.name = "thermal",.class = ACPI_THERMAL_CLASS,.ids = thermal_device_ids,.ops = {.add = acpi_thermal_add,.remove = acpi_thermal_remove,.notify = acpi_thermal_notify,}, .drv.pm = &acpi_thermal_pm,
};7.1.1.2 struct thermal_zone_device_ops acpi_thermal_zone_ops;
//drivers/acpi/thermal.c
static struct thermal_zone_device_ops acpi_thermal_zone_ops = {.bind = acpi_thermal_bind_cooling_device,.unbind = acpi_thermal_unbind_cooling_device,.get_temp = thermal_get_temp,.get_mode = thermal_get_mode,.set_mode = thermal_set_mode,.get_trip_type = thermal_get_trip_type,.get_trip_temp = thermal_get_trip_temp,.get_crit_temp = thermal_get_crit_temp,.get_trend = thermal_get_trend,.notify = thermal_notify,
};7.1.2 ACPI中的 Thermal Objects

《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》11.4 Thermal Objects
7.1.3 驱动初始化大致流程
acpi_thermal_add();-> acpi_thermal_get_info(tz);-> acpi_thermal_get_trip_points(tz); /* Get trip points [_CRT, _PSV, etc.] (required) */-> acpi_thermal_trips_update();-> acpi_evaluate_integer(tz->device->handle, "_CRT", NULL, &tmp);-> tz->trips.critical.temperature = tmp;-> acpi_evaluate_integer(tz->device->handle, "_HOT", NULL, &tmp);-> tz->trips.hot.temperature = tmp;-> acpi_evaluate_integer(tz->device->handle, "_PSV", NULL, &tmp);-> tz->trips.passive.temperature = tmp;-> acpi_thermal_get_temperature(tz); /* Get temperature [_TMP] (required) */-> acpi_evaluate_integer(tz->device->handle, "_TMP", NULL, &tmp);-> tz->temperature = tmp;-> acpi_thermal_set_cooling_mode(); /* Set the cooling mode [_SCP] to active cooling (default) */-> acpi_thermal_register_thermal_zone();-> thermal_zone_device_register("acpitz", trips, 0, tz, &acpi_thermal_zone_ops, ...);-> sysfs_create_link(&tz->device->dev.kobj, &tz->thermal_zone->device.kobj, "thermal_zone");-> sysfs_create_link(&tz->thermal_zone->device.kobj, &tz->device->dev.kobj, "device");7.1.4 ACPI Source Language (ASL)示例
ThermalZone (TZ0) {Method(_TMP) { Return (\_SB.PCI0.ISA0.EC0.TMP )} // get current tempName(_PSL, Package() {\_SB.CPU0, \\_SB.CPU1}) // passive cooling devicesName(_AL0, Package() {\_SB.PCI0.ISA0.EC0.FN1}) // active coolingMethod(_AC0) { Return (\_SB.PCI0.ISA0.EC0.AC0) } // fan temp (high)Method(_AC1) { Return (\_SB.PCI0.ISA0.EC0.AC1) } // fan temp (low)Method(_PSV) { Return (\_SB.PCI0.ISA0.EC0.PSV) } // passive cooling tempMethod(_HOT) { Return (\_SB.PCI0.ISA0.EC0.HOT) } // get critical S4 tempMethod(_CRT) { Return (\_SB.PCI0.ISA0.EC0.CRT) } // get crit. tempName(_TC1, 4) // bogus example constantName(_TC2, 3) // bogus example constantMethod(_SCP, 1) { Store (Arg0, \\_SB.PCI0.ISA0.EC0.MODE) } // set cooling modeName(_TSP, 150) // passive sampling = 15 sec
} // end of TZ0 《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》
11.7.3 Example: Thermal Zone with Multiple Devices
7.2 cooling_device: Fan
7.2.1 数据结构
7.2.1.1 struct platform_driver acpi_fan_driver;
//drivers/acpi/fan.c
static const struct acpi_device_id fan_device_ids[] = {{"PNP0C0B", 0},{"INT3404", 0},{"", 0},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(acpi, fan_device_ids);static struct platform_driver acpi_fan_driver = {.probe = acpi_fan_probe,.remove = acpi_fan_remove,.driver = {.name = "acpi-fan",.acpi_match_table = fan_device_ids,.pm = FAN_PM_OPS_PTR,},
};7.2.1.2 struct thermal_cooling_device_ops fan_cooling_ops;
//drivers/acpi/fan.c
static const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops fan_cooling_ops = {.get_max_state = fan_get_max_state,.get_cur_state = fan_get_cur_state,.set_cur_state = fan_set_cur_state,
};7.2.2 控制风扇的转速(fan_set_cur_state)
7.2.2.1 简介
在ACPI规范中Device Power States有四种


《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》 A.2 Device Power States
7.2.2.2 控制固定转速的风扇
对于固定转速的风扇,控制起来很方便,进入D0状态就是打开风扇,进入D3状态就是关闭风扇。
fan_set_cur_state();-> fan_set_state();static int fan_set_state(struct acpi_device *device, unsigned long state)
{if (state != 0 && state != 1)return -EINVAL;return acpi_device_set_power(device,state ? ACPI_STATE_D0 : ACPI_STATE_D3_COLD);
}7.2.2.3 ACPI 1.0版本下控制可调转速的风扇
ACPI 1.0 defined a simple fan device that is assumed to be in operation when it is in the D0 state. Thermal zones reference fan device(s) as being responsible primarily for cooling within that zone.Notice that multiple fan devices can be present for any one thermal zone. They might be actual different fans, or they might be used to implement one fan of multiple speeds (for example, by turning both “fans” on the one fan will run full speed).
《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》11.3 Fan Device
示例
// Following is a single fan with two speeds. This is represented
// by creating two logical fan devices. When FN2 is turned on then
// the fan is at a low speed. When FN1 and FN2 are both on then
// the fan is at high speed.
//
// Create FAN device object FN1
Device (FN1) {// Device ID for the FANName(_HID, EISAID("PNP0C0B"))Name(_UID, 0)Name(_PR0, Package(){FN10, FN11})
}
// Create FAN device object FN2
Device (FN2) {// Device ID for the FANName(_HID, EISAID("PNP0C0B"))Name(_UID, 1)Name(_PR0, Package(){FN10})
}《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》11.7.2 Example: Multiple-Speed Fans
7.2.2.4 ACPI 4.0版本下控制可调转速的风扇
ACPI 4.0添加了4个Fan Objects来描述风扇信息,其中“_FPS (Fan Performance States)”可以描述一个风扇支持的多个转速信息。
Package {Revision, // Integer - Current revision is: 0FanPState[0], // Package......FanPState[n] // Package
}Each FanPState sub-Package contains the elements described below:
Package () // Fan P-State
{Control, // Integer DWORDTripPoint, // Integer DWORDSpeed, // Integer DWORDNoiseLevel, // Integer DWORDPower // Integer DWORD
}《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》11.3.1 Fan Objects
驱动流程
fan_set_cur_state();-> fan_set_state_acpi4();7.2.3 驱动初始化大致流程
acpi_fan_probe(); -> acpi_fan_get_fps(); //get _FPS (Fan Performance States)-> acpi_evaluate_object(device->handle, "_FPS", NULL, &buffer);-> fan->fps_count = obj->package.count - 1;-> thermal_cooling_device_register(name, device, &fan_cooling_ops);7.2.4 ACPI Source Language (ASL)示例
请看上面的“7.2.2.3”小节
7.3 cooling_device: Processor
7.3.1 数据结构
//drivers/acpi/processor_thermal.c
static const struct acpi_device_id processor_device_ids[] = {{ACPI_PROCESSOR_OBJECT_HID, 0}, //ACPI_PROCESSOR_OBJECT_HID "LNXCPU"{ACPI_PROCESSOR_DEVICE_HID, 0}, //ACPI_PROCESSOR_DEVICE_HID "ACPI0007"{"", 0},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(acpi, processor_device_ids);static struct device_driver acpi_processor_driver = {.name = "processor",.bus = &cpu_subsys,.acpi_match_table = processor_device_ids,.probe = acpi_processor_start,.remove = acpi_processor_stop,
};const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops processor_cooling_ops = { .get_max_state = processor_get_max_state,.get_cur_state = processor_get_cur_state,.set_cur_state = processor_set_cur_state,
};7.3.2 初始化流程
acpi_processor_driver_init(void); //module_init(acpi_processor_driver_init);-> driver_register(&acpi_processor_driver);-> acpi_processor_start();-> __acpi_processor_start();-> acpi_pss_perf_init();-> acpi_processor_get_throttling_info();-> acpi_processor_get_throttling_states();-> acpi_evaluate_object(pr->handle, "_TSS", NULL, &buffer);-> pr->throttling.state_count = tss->package.count;-> thermal_cooling_device_register("Processor", device, &processor_cooling_ops);7.3.3 ACPI Source Language (ASL)示例
Scope(\_SB) {Device(CPU0) {Name(_HID, "ACPI0007")Name(_UID, 0)//// Load additional objects if 3.0 Thermal model support is available//Method(_INI, 0) {If (\_OSI("3.0 Thermal Model")) {LoadTable("OEM1", "PmRef", "Cpu0", "\\_SB.CPU0") // 3.0 Thermal Model}}// For brevity, most processor objects have been excluded// from this example (such as \_PSS, \_CST, \_PCT, \_PPC, etc.)// Processor Throttle Control objectName(_PTC, ResourceTemplate() {Register(SystemIO, 32, 0, 0x120) // Processor ControlRegister(SystemIO, 32, 0, 0x120) // Processor Status})// Throttling Supported States// The values shown are for exemplary purposes onlyName(_TSS, Package() {// Read: freq percentage, power, latency, control, statusPackage() {0x64, 1000, 0x0, 0x7, 0x0}, // Throttle off (100%)Package() {0x58, 800, 0x0, 0xF, 0x0}, // 87.5%Package() {0x4B, 600, 0x0, 0xE, 0x0}, // 75%Package() {0x3F, 400, 0x0, 0xD, 0x0} // 62.5%})// Throttling Present Capabilities// The values shown are for exemplary purposes onlyMethod(_TPC) {If(\_SB.AC) {Return(0) // All throttle states available} Else {Return(2) // Throttle states >= 2 are available} } } // end of CPU0 scope......
} 《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》
11.7.3 Example: Thermal Zone with Multiple Devices
8 通过设备树(DTS)指定硬件信息的温控驱动分析
8.1 thermal_zone_device
8.1.1 数据结构
//drivers/thermal/of-thermal.c
static struct thermal_zone_device_ops of_thermal_ops = {.get_mode = of_thermal_get_mode,.set_mode = of_thermal_set_mode,.get_trip_type = of_thermal_get_trip_type,.get_trip_temp = of_thermal_get_trip_temp,.set_trip_temp = of_thermal_set_trip_temp,.get_trip_hyst = of_thermal_get_trip_hyst,.set_trip_hyst = of_thermal_set_trip_hyst,.get_crit_temp = of_thermal_get_crit_temp,.bind = of_thermal_bind,.unbind = of_thermal_unbind,
};8.1.2 初始化流程
thermal_init(); //fs_initcall(thermal_init);-> of_parse_thermal_zones();-> of_find_node_by_name(NULL, "thermal-zones");-> thermal_of_build_thermal_zone();-> of_property_read_u32(np, "polling-delay-passive", &prop);-> of_property_read_u32(np, "polling-delay", &prop);-> of_property_read_u32_array(np, "coefficients", coef, 2);-> child = of_get_child_by_name(np, "trips");-> thermal_of_populate_trip();-> of_property_read_u32(np, "temperature", &prop); //获取trip point温度值-> of_property_read_u32(np, "hysteresis", &prop);-> thermal_of_get_trip_type();-> of_property_read_string(np, "type", &t); //获取trip point类型(active、passive、hot和critical)-> child = of_get_child_by_name(np, "cooling-maps");-> thermal_of_populate_bind_params();-> of_property_read_u32(np, "contribution", &prop);-> of_count_phandle_with_args(np, "cooling-device", "#cooling-cells");-> of_parse_phandle_with_args(np, "cooling-device", "#cooling-cells", i, &cooling_spec);-> __tcbp[i].cooling_device = cooling_spec.np;-> __tcbp[i].min = cooling_spec.args[0]; //minimum cooling state-> __tcbp[i].max = cooling_spec.args[1]; //maximum cooling state-> __tbp->tcbp = __tcbp;-> thermal_zone_device_register();温度传感器的初始化
thermal_zone_of_sensor_register();-> np = of_find_node_by_name(NULL, "thermal-zones");-> of_parse_phandle_with_args(child, "thermal-sensors", "#thermal-sensor-cells", 0, &sensor_specs);-> thermal_zone_of_add_sensor();-> tz->ops = ops;-> tzd->ops->get_temp = of_thermal_get_temp;-> tzd->ops->get_trend = of_thermal_get_trend;8.1.3 设备树示例
thermal-zones {cpu_thermal: cpu-thermal {polling-delay-passive = <250>; /* milliseconds */polling-delay = <1000>; /* milliseconds */thermal-sensors = <&bandgap0>;trips {cpu_alert0: cpu-alert0 {temperature = <90000>; /* millicelsius */hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */type = "active";}; cpu_alert1: cpu-alert1 {temperature = <100000>; /* millicelsius */hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */type = "passive";}; cpu_crit: cpu-crit {temperature = <125000>; /* millicelsius */hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */type = "critical";}; }; cooling-maps {map0 {trip = <&cpu_alert0>;cooling-device = <&fan0 THERMAL_NO_LIMIT 4>; }; map1 {trip = <&cpu_alert1>;cooling-device = <&fan0 5 THERMAL_NO_LIMIT>, <&cpu0 THERMAL_NO_LIMIT THERMAL_NO_LIMIT>;}; }; };
};Documentation/devicetree/bindings/thermal/thermal.txt
8.2 cooling_device: pwm-fan
8.2.1 数据结构
//drivers/hwmon/pwm-fan.c
static const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops pwm_fan_cooling_ops = {.get_max_state = pwm_fan_get_max_state,.get_cur_state = pwm_fan_get_cur_state,.set_cur_state = pwm_fan_set_cur_state,
};8.2.2 初始化
pwm_fan_probe();-> pwm_fan_of_get_cooling_data();-> of_property_read_u32_array(np, "cooling-levels", ctx->pwm_fan_cooling_levels, num); //获取cooling device支持的state-> devm_thermal_of_cooling_device_register(..., "pwm-fan", ctx, &pwm_fan_cooling_ops);8.2.3 设备树示例
请看“3.3.2.1” 小节
8.3 cooling_device: thermal-cpufreq
8.3.1 数据结构
//drivers/thermal/cpu_cooling.c
static struct thermal_cooling_device_ops cpufreq_cooling_ops = { .get_max_state = cpufreq_get_max_state,.get_cur_state = cpufreq_get_cur_state,.set_cur_state = cpufreq_set_cur_state,
};8.3.2 初始化流程
cpufreq_online();-> of_cpufreq_cooling_register();-> __cpufreq_cooling_register();-> freq_qos_add_request();-> thermal_of_cooling_device_register();8.3.3 设备树示例
请看 “3.3.2.2” 小节
9 调试
9.1 /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/thermal

9.2 /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/thermal_power_allocator/
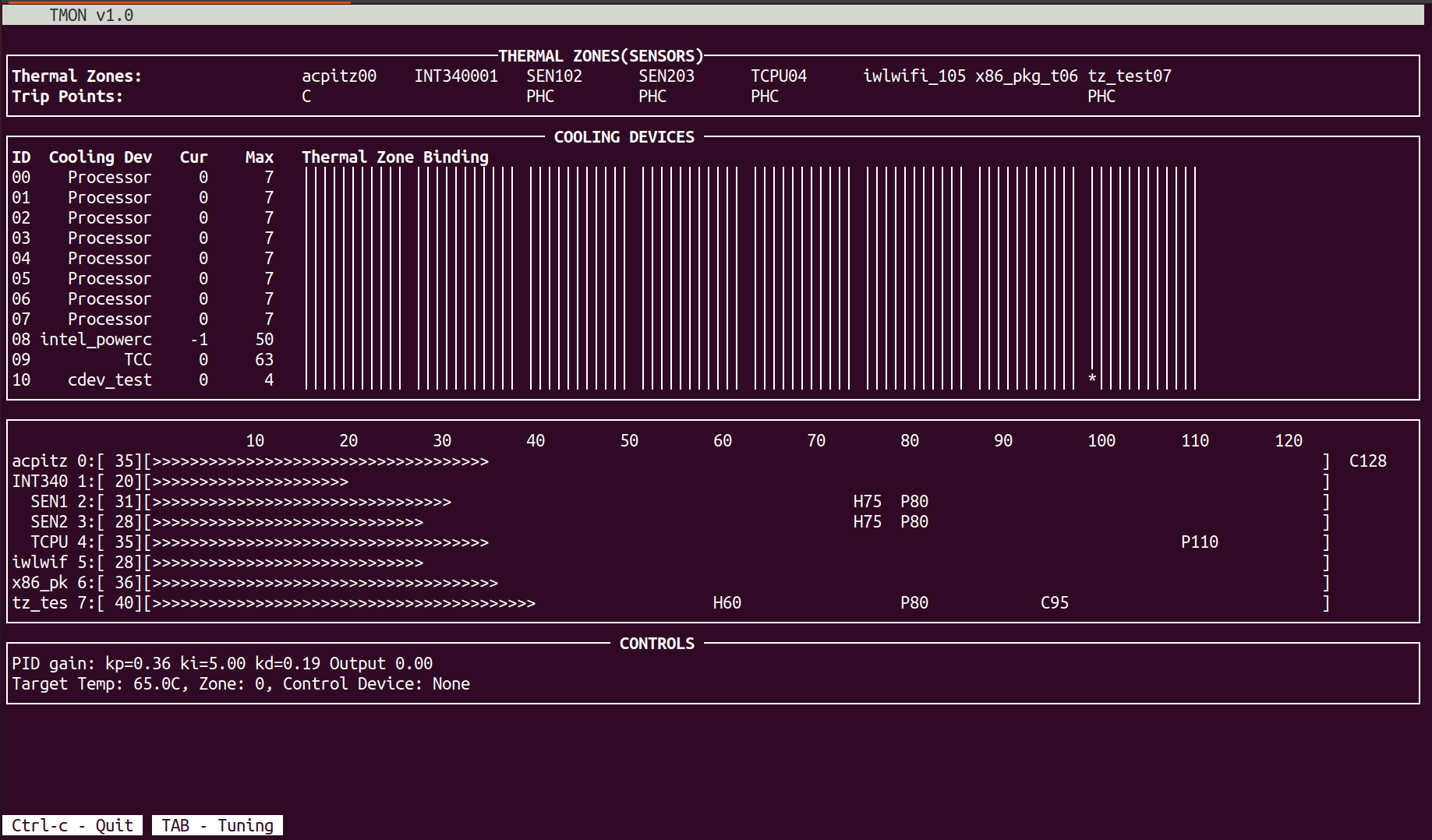
9.3 tmon
tomon工具可以显示下面的信息:
- 实时显示Thermal Zone(温度传感器)获取的温度
- Thermal Zone的trip points
- Cooling device的states信息(current state和 max state)
- Cooling device 和 Thermal zone的绑定关系
⼯具源码:<kernel_src>/tools/thermal/tmon
执行命令“ ./tools/thermal/tmon/tmon” 后会显示下面的界面
相关文章:
,发热管理(thermal),温度控制)
Linux电源管理(五),发热管理(thermal),温度控制
更多linux系统电源管理相关的内容请看:Linux电源管理、功耗管理 和 发热管理 (CPUFreq、CPUIdle、RPM、thermal、睡眠 和 唤醒)-CSDN博客 本文主要基于linux-5.4.18版本的内核代码进行分析。 1 简介 1.1 硬件知识 CPU等芯片在工作时会产生大量热量,…...

【C++11】异常
前言 上文我们学习到了C11中类的新功能【C11】类的新功能-CSDN博客 本文我们来学习C下一个新语法:异常 1.异常的概念 异常的处理机制允许程序在运行时就出现的问题进行相应的处理。异常可以使得我们将问题的发现和问题的解决分开,程序的一部分负…...

C#WPF里不能出现滚动条的原因
使用下面这段代码,就不能出现滚动条: <mdix:DrawerHost.LeftDrawerContent><Grid Width="260" Background="{StaticResource MaterialDesign.Brush.Primary}"><Grid.RowDefinitions><RowDefinition Height="auto"/>&l…...

安装Hadoop并运行WordCount程序
一、安装 Java Hadoop 依赖 Java,首先需要安装 Java 开发工具包(JDK)。以 Ubuntu 为例: bash sudo apt update sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk安装后,设置环境变量: bash echo export JAVA_HOME/usr/li…...

从零搭建AI工作站:Gemma3大模型本地部署+WebUI配置全套方案
文章目录 前言1. 安装Ollama2.Gemma3模型安装与运行3. 安装Open WebUI图形化界面3.1 Open WebUI安装运行3.2 添加模型3.3 多模态测试 4. 安装内网穿透工具5. 配置固定公网地址总结 前言 如今各家的AI大模型厮杀得如火如荼,每天都有新的突破。今天我要给大家安利一款…...

《数字人技术实现路径深度剖析与研究报告》
《数字人技术实现路径深度剖析与研究报告》 一、引言 1.1 研究背景与意义 近年来,随着人工智能、虚拟现实、计算机图形学等技术的飞速发展,数字人技术应运而生并取得了显著进展。数字人作为一种新兴的技术应用,正逐步渗透到各个领域,成为推动行业创新发展的重要力量。从最…...

《棒球百科》MLB棒球公益课·棒球1号位
MLB(美国职业棒球大联盟)的棒球公益课通过推广棒球运动、普及体育教育,对全球多个地区产生了多层次的影响: 1. 体育文化推广 非传统棒球地区的普及:在棒球基础较弱的地区(如中国、欧洲部分国家)…...
内存泄漏问题及解决方案)
Android 中 Handler (创建时)内存泄漏问题及解决方案
一、Handler 内存泄漏核心原理 真题 1:分析 Handler 内存泄漏场景 题目描述: 在 Activity 中使用非静态内部类 Handler 发送延迟消息,旋转屏幕后 Activity 无法释放,分析原因并给出解决方案。 内存泄漏链路分析: 引…...
)
linux-驱动开发之设备树详解(RK平台为例)
前言 Linux3.x以后的版本才引入了设备树,设备树用于描述一个硬件平台的板级细节。 在早些的linux内核,这些“硬件平台的板级细节”保存在linux内核目录“/arch”, 以ARM为例“硬件平台的板级细节”保存在“/arch/arm/plat-xxx”和“/arch/ar…...

【现代深度学习技术】注意力机制05:多头注意力
【作者主页】Francek Chen 【专栏介绍】 ⌈ ⌈ ⌈PyTorch深度学习 ⌋ ⌋ ⌋ 深度学习 (DL, Deep Learning) 特指基于深层神经网络模型和方法的机器学习。它是在统计机器学习、人工神经网络等算法模型基础上,结合当代大数据和大算力的发展而发展出来的。深度学习最重…...

RDD的五大特征
1. 由多个分区(Partitions)组成 特性:RDD 是分区的集合,每个分区在集群的不同节点上存储。分区是数据并行处理的基本单位。作用:分区使 RDD 能够在集群中并行计算,提高处理效率。 2. 有一个计算每个分区的…...
)
键盘RGB矩阵与LED指示灯(理论部分)
键盘RGB矩阵与LED指示灯(理论部分) 一、LED指示灯基础 在键盘世界里,LED指示灯不仅仅是装饰,它们还能提供丰富的状态信息。QMK固件提供了读取HID规范中定义的5种LED状态的方法: Num Lock(数字锁定)Caps Lock(大写锁定)Scroll Lock(滚动锁定)Compose(组合键)Desp…...
)
HTTP方法和状态码(Status Code)
HTTP方法 HTTP方法(也称HTTP动词)主要用于定义对资源的操作类型。根据HTTP/1.1规范(RFC 7231)以及后续扩展,常用的HTTP方法有以下几种: GET:请求获取指定资源的表示形式。POST:向指…...

【sqlmap需要掌握的参数】
sqlmap需要掌握的参数 目标-u 指定URL 用于get请求-l 用于post请求- r 用于post请求指定数据库/表/字段 -D/-T/-C 脱库获得数据库获取用户获取表获取列获取字段获取字段类型获取值 其他 目标 -u 指定URL 用于get请求 -u URL, --urlURL 目标URL 只使用于get命令中 -l 用于pos…...

用 AltSnap 解锁 Windows 窗口管理的“魔法”
你有没有遇到过这样的场景:电脑屏幕上堆满了窗口,想快速调整它们的大小和位置,却只能拖来拖去,费时又费力?或者你是个多任务狂魔,喜欢一边写代码、一边看文档、一边刷视频,却发现 Windows 自带的…...
:TLS无锁访问以及Central Cache结构设计)
高并发内存池(三):TLS无锁访问以及Central Cache结构设计
目录 前言: 一,thread cache线程局部存储的实现 问题引入 概念说明 基本使用 thread cache TLS的实现 二,Central Cache整体的结构框架 大致结构 span结构 span结构的实现 三,Central Cache大致结构的实现 单例模式 thr…...

数据治理域——数据治理体系建设
摘要 本文主要介绍了数据治理系统的建设。数据治理对企业至关重要,其动因包括应对数据爆炸增长、提升内部管理效率、支撑复杂业务需求、加强风险防控与合规管理以及实现数字化转型战略。其核心目的是提升数据质量、统一数据标准、优化数据资产管理、支撑业务发展和…...

数据库实验报告 SQL SERVER 2008的基本操作 1
实验报告(第 1 次) 实验名称 SQL SERVER 2008的基本操作 实验时间 9月14日1-2节 一、实验内容 数据库的基本操作:包括创建、修改、附加、分离和删除数据库等。 二、源程序及主要算法说明 本次实验不涉及程序和算法。 三、测…...

基于STM32、HAL库的ICP-20100气压传感器 驱动程序设计
一、简介: ICP-20100 是 InvenSense(TDK 集团旗下公司)生产的一款高精度数字气压传感器,专为需要精确测量气压和海拔高度的应用场景设计。它具有低功耗、高精度、快速响应等特点,非常适合物联网、可穿戴设备和无人机等应用。 二、硬件接口: ICP-20100 引脚STM32L4XX 引脚…...

提示工程实战指南:Google白皮书关键内容一文讲清
You don’t need to be a data scientist or a machine learning engineer – everyone can writea prompt. 一、概述 Google于2025年2月发布的《Prompt Engineering》白皮书系统阐述了提示工程的核心技术、实践方法及挑战应对策略。该文档由Lee Boonstra主编,多位…...

国产大模型「五强争霸」:决战AGI,谁主沉浮?
引言 中国AI大模型市场正经历一场史无前例的洗牌!曾经“百模混战”的局面已落幕,字节、阿里、阶跃星辰、智谱和DeepSeek五大巨头强势崛起,形成“基模五强”新格局。这场竞争不仅是技术实力的较量,更是资源、人才与生态的全面博弈。…...
、设置阻塞/非阻塞)
Linux进程10-有名管道概述、创建、读写操作、两个管道进程间通信、读写规律(只读、只写、读写区别)、设置阻塞/非阻塞
目录 1.有名管道 1.1概述 1.2与无名管道的差异 2.有名管道的创建 2.1 直接用shell命令创建有名管道 2.2使用mkfifo函数创建有名管道 3.有名管道读写操作 3.1单次读写 3.2多次读写 4.有名管道进程间通信 4.1回合制通信 4.2父子进程通信 5.有名管道读写规律ÿ…...

高吞吐与低延迟的博弈:Kafka与RabbitMQ数据管道实战指南
摘要 本文全面对比Apache Kafka与RabbitMQ在数据管道中的设计哲学、核心差异及协同方案。结合性能指标、应用场景和企业级实战案例,揭示Kafka在高吞吐流式处理中的优势与RabbitMQ在复杂路由和低延迟传输方面的独特特点;介绍了使用Java生态成熟第三方库&…...
 深入解析)
C++23 views::slide (P2442R1) 深入解析
文章目录 引言C20 Ranges库回顾什么是Rangesstd::views的作用 views::slide 概述基本概念原型定义辅助概念工作原理代码示例输出结果 views::slide 的应用场景计算移动平均值查找连续的子序列 总结 引言 在C的发展历程中,每一个新版本都会带来一系列令人期待的新特…...

SpringDataRedis的入门案例,以及RedisTemplate序列化实现
目录 SpringDataRedis 简单介绍 入门案例 RedisTemplate序列化方案 方案一: 方案二: SpringDataRedis 简单介绍 提供了对不同Redis客户端的整合(Lettuce和Jedis) 提供了RedisTemplate统一API来操作Redis 支持Redis的发布订阅模型 支持Redis哨兵和Redis集群 支持基于…...

鸿蒙HarmonyOS list优化一: list 结合 lazyforeach用法
list列表是开发中不可获取的,非常常用的组件,使用过程中会需要不断的优化,接下来我会用几篇文章进行list在纯原生的纯血鸿蒙的不断优化。我想进大厂,希望某位大厂的看到后能给次机会。 首先了解一下lazyforeach: Laz…...

【Jenkins简单自动化部署案例:基于Docker和Harbor的自动化部署流程记录】
摘要 本文记录了作者使用Jenkins时搭建的一个简单自动化部署案例,涵盖Jenkins的Docker化安装、Harbor私有仓库配置、Ansible远程部署等核心步骤。通过一个SpringBoot项目 (RuoYi) 的完整流程演示,从代码提交到镜像构建、推送、滚动更新,逐步实…...

【愚公系列】《Manus极简入门》034-跨文化交流顾问:“文化桥梁使者”
🌟【技术大咖愚公搬代码:全栈专家的成长之路,你关注的宝藏博主在这里!】🌟 📣开发者圈持续输出高质量干货的"愚公精神"践行者——全网百万开发者都在追更的顶级技术博主! …...

数字滤波器应用介绍
此示例说明如何设计、分析数字过滤器并将其应用于数据。它将帮助您回答以下问题: 如何补偿滤波器引入的延迟?如何避免使信号失真?如何从信号中删除不需要的内容?如何微分信号?以及积分信号文章目录 补偿筛选引入的延迟补偿恒定滤波器延迟 如FIR引起的消除方法,末尾添零补…...

木马查杀篇—Opcode提取
【前言】 介绍Opcode的提取方法,并探讨多种机器学习算法在Webshell检测中的应用,理解如何在实际项目中应用Opcode进行高效的Webshell检测。 Ⅰ 基本概念 Opcode:计算机指令的一部分,也叫字节码,一个php文件可以抽取出…...
)
栈和队列复习(C语言版)
目录 一.栈的概念 二.栈的实现 三.队列的概念 四.队列的实现 五.循环队列的实现 一.栈的概念 可以将栈抽象地理解成羽毛球桶,或者理解成坐直升电梯;最后一个进去的,出来时第一个出来,并且只有一个出入口。这边需要注意的是&am…...

SDK does not contain ‘libarclite‘ at the path
Xcode16以上版本更新SDK之后就报错了。是因为缺少libarclite_iphoneos.a文件。所以需要在网上找一下该文件根据路径添加进去,arc文件可能需要新建一下。 clang: error: SDK does not contain ‘libarclite’ at the path ‘/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Develo…...

Kotlin跨平台Compose Multiplatform实战指南
Kotlin Multiplatform(KMP)结合 Compose Multiplatform 正在成为跨平台开发的热门选择,它允许开发者用一套代码构建 Android、iOS、桌面(Windows/macOS/Linux)和 Web 应用。以下是一个实战指南,涵盖核心概念…...

Oracle数据库全局性HANG的处理过程
如果Oracle数据库全局性HANG,首先要做的就是收集数据库HANG时的状态,只有收集到了相应状态,抓住故障现场,才可以进一步分析故障产生的可能原因。 出现此故障,一般情况下可以如此处理: 如果数据库是单节点&a…...
英文题库(21-30))
MySQL 8.0 OCP(1Z0-908)英文题库(21-30)
目录 第21题题目分析正确答案 第22题题目分析正确答案 第23题题目分析正确答案 第24题题目分析正确答案 第25题题目分析正确答案 第26题题目分析正确答案 第27题题目分析正确答案 第28题题目分析正确答案 第29题题目分析正确答案 第30题题目解析正确答案 第21题 Choose three.…...
)
beyond compare 免密钥进入使用(删除注册表)
beyond compare 免密钥进入,免费使用(删除注册表) 温馨提醒:建议仅个人使用,公司使用小心律师函警告! 1.winr 输入regedit 打开注册表 2.删除计算机 \HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Scooter Software\Beyo…...

前端项目2-01:个人简介页面
目录 一.代码显示 二.效果图 三.代码分析 1. 文档声明和 HTML 基本结构 2. CSS 样式部分 全局样式 body 样式 页面主要容器 box 样式 左侧区域 l 样式 右侧区域 r 样式 左侧区域中头像容器 to 样式 头像图片样式及悬停效果 左侧区域中个人信息容器 tit 样式 个人…...

.NET 8 API 实现websocket,并在前端angular实现调用
.NET 8 API 实现websocket,并在前端angular实现调用。 后端:.NET 8 WebSocket API 实现 在 .NET 8 中,可以通过 Microsoft.AspNetCore.WebSockets 提供的支持来实现 WebSocket 功能。以下是创建一个简单的 WebSocket 控制器的步骤。 安装必…...

P2P架构
P2P 是 Peer-to-Peer(点对点) 的缩写,是一种 去中心化 的网络架构,其中每个节点(称为 “对等节点”,Peer)既是 “客户端”,也是 “服务器”,可以直接与其他节点通信、共享…...

菊厂0510面试手撕题目解答
题目 输入一个整数数组,返回该数组中最小差出现的次数。 示例1:输入:[1,3,7,5,9,12],输出:4,最小差为2,共出现4次; 示例2:输入:[90,98,90,90,1,1]…...
VPN虚拟专用网 L2TP、PPTP、PPP认证方式;IPSec、GRE)
【25软考网工】第六章(4)VPN虚拟专用网 L2TP、PPTP、PPP认证方式;IPSec、GRE
博客主页:christine-rr-CSDN博客 专栏主页:软考中级网络工程师笔记 大家好,我是christine-rr !目前《软考中级网络工程师》专栏已经更新二十多篇文章了,每篇笔记都包含详细的知识点,希望能帮助到你!…...
)
C语言:深入理解指针(3)
目录 一、数组名的理解 二、用指针访问数组 三、一维数组传参的本质 四、冒泡排序 五、二级指针 六、指针数组 七、指针数组模拟二维数组 八、结语 一、数组名的理解 数组名其实就是首元素的地址 int arr[3] {1,2,3}; printf("arr :%p\n" ,arr); printf(…...
)
R语言实战第5章(1)
第一部分:数学、统计和字符处理函数 数学和统计函数:R提供了丰富的数学和统计函数,用于执行各种计算和分析。这些函数可以帮助用户快速完成复杂的数学运算、统计分析等任务,例如计算均值、方差、相关系数、进行假设检验等。字符处…...

Lodash isEqual 方法源码实现分析
Lodash isEqual 方法源码实现分析 Lodash 的 isEqual 方法用于执行两个值的深度比较,以确定它们是否相等。这个方法能够处理各种 JavaScript 数据类型,包括基本类型、对象、数组、正则表达式、日期对象等,并且能够正确处理循环引用。 1. is…...

探索边缘计算:赋能物联网的未来
摘要 随着物联网(IoT)技术的飞速发展,越来越多的设备接入网络,产生了海量的数据。传统的云计算模式在处理这些数据时面临着延迟高、带宽不足等问题,而边缘计算的出现为解决这些问题提供了新的思路。本文将深入探讨边缘…...

Ubuntu中配置【Rust 镜像源】
本篇主要记录Ubuntu中配置Rust编程环境时,所需要做的镜像源相关的配置 无法下载 Rust 工具链 通过环境变量指定 Rust 的国内镜像源(如中科大或清华源)。 方法一:临时设置镜像 export RUSTUP_DIST_SERVERhttps://mirrors.ustc.e…...

netty 客户端发送消息服务端收到消息无法打印,springBoot配合 lombok使用@Slf4j
netty 客户端发送消息服务端收到消息无法打印,springBoot配合 lombok使用Slf4j 服务端代码 Slf4j public class EventLoopServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {new ServerBootstrap().group(new NioEventLoopGroup()).c…...
)
学习笔记:黑马程序员JavaWeb开发教程(2025.4.3)
12.1 基础登录功能 EmpService中的login方法,是根据接收到的用户名和密码,查询时emp数据库中的员工信息,会返回一个员工对象。使用了三元运算符来写返回 Login是登录,是一个业务方法,mapper接口是持久层,是…...
)
Spark SQL 运行架构详解(专业解释+番茄炒蛋例子解读)
1. 整体架构概览 Spark SQL的运行过程可以想象成一个"SQL查询的加工流水线",从原始SQL语句开始,经过多个阶段的处理和优化,最终变成分布式计算任务执行。主要流程如下: SQL Query → 解析 → 逻辑计划 → 优化 → 物理…...
字符数组的输入输出)
【时时三省】(C语言基础)字符数组的输入输出
山不在高,有仙则名。水不在深,有龙则灵。 ----CSDN 时时三省 字符数组的输入输出可以有两种方法。 ( 1 )逐个字符输入输出。用格式符“% c”输入或输出一个字符. ( 2 )将整个字符串一次输入或输出。用“% s”格式符,意思是对字符串( strin…...
